Concrete steps are an essential addition to modern homes and outdoor landscapes, valued for their durability and versatility.
Whether constructed as cement steps for entrances, prefab concrete steps for gardens, or elaborate floating staircases, concrete steps offer enduring strength and aesthetic appeal for any residential or commercial setting.
Why Choose Concrete Steps?
The main reasons to choose concrete steps are durability, affordability, and ease of maintenance. Compared to wood or steel stairs, concrete steps resist weathering, fire, and pests, making them ideal for outdoor use and high-traffic areas.
- Concrete steps stand up to decades of use with minimal repairs, retaining their structural integrity.
- Their robust nature means less frequent maintenance than materials like timber, saving homeowners time and money.
- Fire resistance and slip-proof surfaces enhance safety, especially around doorsteps and home entries.
Versatility and Design
Concrete stair treads and precast steps allow endless design possibilities. From traditional styles like concrete stoops to modern floating staircases, concrete adapts to diverse architectural needs. Precast concrete staircases, crafted off-site, can mimic natural stone or be polished for a contemporary look.
- You can choose between floating staircase designs suitable for open interiors or classic concrete steps designed for houses.
- With options for incorporating stepping stones or custom concrete stair treads, homeowners get both function and style.
- Design flexibility allows integration with craftsman-style exterior features, tailored doorsteps, and bespoke precast steps.
Concrete steps are a staple of outdoor design, offering robust, weather-resistant access for buildings, patios, and landscaped spaces.
Whether building a simple exterior pathway or a dramatic concrete staircase outdoors, understanding design, dimension, reinforcement, and construction is crucial for lasting results that comply with safety and aesthetic standards.
What are Concrete Steps?
Concrete steps are solid stairways cast onsite or precast in a factory, then installed at entrances, patios, public spaces, and gardens. People recognize these sturdy structures for their reliable strength, customizable appearance, and long lifespan.
Outdoor Concrete Stairs: Purpose and Flexibility
Outdoor concrete stairs, including the classic outdoor concrete staircase, efficiently handle heavy foot traffic, changes in elevation, and weather extremes.
While concrete steps feel rigid and supportive (they are not flexible when stepped on, thanks to steel reinforcement and material density), their structural flexibility lies in design variations and adapting layouts for different uses and aesthetics.
Typical Concrete Step Design Details
Standard Dimensions
The design of concrete stairs outdoors involves key measurements to maximize comfort and safety:
- Riser height: Standard is 6″ to 7.5″ (15-19 cm). For public stairs, risers are often 14-15 cm (5.5-6″) for ease of movement.
- Tread depth: Commonly 10″ to 11″ (25-28 cm). Public areas may use up to 30 cm (12″) for safer footing.
- Width: Minimum of 36″ (91 cm), wider for public spaces.
- Step thickness: For reinforced exterior steps, the minimum is 2″ (5 cm); thicker (4-6″, 10-15 cm) for structural or overlay applications.
- Porch step height: Often 7″ (18 cm) for comfort.
- Slab thickness for stone steps: Minimum 4″ (10 cm).
Grade and Elevation
For stairs on grade and pathways, steps should be sized to accommodate surface slopes and provide level landings. Guidelines for concrete step elevations ensure water drains away, preventing pooling and slip hazards.
Concrete Outdoor Steps Construction Detail
A resilient exterior concrete staircase system involves:
- Formwork constructed from timber or metal, shaped precisely to the desired profile
- Proper base preparation (compacted gravel or concrete slab) for foundation stability
- Placement of steel reinforcement bars (rebar) to prevent cracking and improve load-bearing
- Pouring a high-performance concrete mix suitable for exterior use (low water-cement ratio, air entrainment for freeze-thaw resistance, best concrete mix for stairs)
- Vibration and leveling for smooth, air-bubble-free finish
- Curing for 7-10 days with moisture retention for strength
Reinforcing Concrete Steps
Do outdoor concrete stairs need reinforcing in the steps?
Yes. Steel bars (main and distribution) are crucial for strength and durability, especially for wider spans, heavy loads, and visible outdoor public concrete stairs.
Reinforcement follows local codes and standards, with minimum cover for steel (15 mm+), ties for nosing, and dowel bars anchoring to landings.
Aesthetics: External Concrete Steps and Landscaping
The aesthetics of external concrete steps can be enhanced with:
- Stamped or colored concrete finishes
- Integrated lighting under treads
- Edges and nosing with bullnose profiles
- Landscaping integration of steps, terraces, and walkways
- Decorative railings paired with exterior pathways
Design and Layout Considerations
Typical Paved Steps Details
- For patios and terraces, step size for a patio aims for a riser of 14-18 cm, a tread of 28-30 cm (depth), and 30-36 cm (width).
- Lay out concrete steps using continuous, evenly spaced risers and treads for safety.
- Concrete steps Different lengths accommodate site constraints.
- Outdoor concrete stair foundation detail includes a solid concrete base, sloped for drainage, and properly compacted fill beneath.
Common Questions
Are exterior concrete steps flexible when you step on them?
No, concrete steps are not flexible due to their rigid, reinforced structure. Any flexibility would indicate a structural issue and should be addressed immediately.
What is the typical tread for outdoor cement stairs?
A typical outdoor concrete tread is 11″ (28 cm). Treads wider than the pathway can be used for aesthetic appeal and easier movement.
How thick is a weather step?
For all-weather durability, outdoor concrete steps should be at least 4″ (10 cm) thick.
What height should concrete steps be?
Best practice for outdoor steps is a 7″ (18 cm) riser height, with tread depths of 10-12″ (25-30 cm).
How thick should a back porch step be?
Back porch steps should be a minimum of 4″ (10 cm) thick for durability and safe load-bearing.
Exterior Public Concrete Stairs and Entryways
For public entryways and sidewalks, sidewalk stair design and exterior public concrete stairs require larger, more robust steps—wider, deeper treads, gentle risers, non-slip finishes, and strong reinforcement.
Concrete Stairs Design: Modern Trends
Modern exterior concrete stair designs include:
- Floating steps for contemporary look
- Integration with landscaping for seamless surroundings
- Spiral or curved configurations for compact spaces
- Exposed aggregate or polished surfaces for visual appeal
The Benefits of Precast Concrete Steps
Prefab concrete steps and precast concrete steps offer significant advantages:
- Fast, weather-independent installation, ready for immediate use—even during unfavorable conditions.
- Controlled factory production ensures quality, consistency, and uniform appearance, which are critical for projects where aesthetics matter.
- Customizable treads, risers, colors, and surface textures meet specific site requirements and personal preferences.
Types of Concrete Steps for Houses
Choosing the right concrete steps for houses depends on function and style:
- Steppers and stepping stones create pathways or garden entries, offering both utility and decorative value.
- Full-size concrete stairs serve as robust access between multi-level spaces, while smaller concrete stoops add curb appeal to home entrances.
- Customized floating staircases add architectural interest indoors, requiring expert installation.
- Precast concrete steps can be tailored to specific heights and widths, designed for easy doorstep transitions and safe house entry.
Craftsman Quality and Long-Term Value
Superior craftsman standards ensure precast steps meet stringent durability and safety guidelines. Leading manufacturers design steps compatible with all building codes and styles, from painted finishes to exposed aggregate surfaces.
- High-grade materials and engineering ensure long-lasting concrete steps and stair treads.
- Homeowners benefit from reduced waste, minimal labor, and cost-effective installation compared to site-cast concrete.
- Quality assurance procedures and customizable options maximize project value from garden steppers to elaborate stairs.
Properly designing and constructing residential concrete steps requires adhering to certain best practices related to layout, dimensions, structural integrity, aesthetics, and safety.

Design considerations of concrete steps
- Step Dimensions—Determine the appropriate tread depth, riser height, and step width to meet safety codes and intended use. Consider visibility needs and accessibility.
- Layout—Steps must transition smoothly between landings and conform to terrain contours. Straight runs or necessary switchbacks should orient with major foot traffic patterns when possible.
- Foundation—Reinforced foundations beneath steps distribute structural loads properly without shifting or settling over time. This prevents cracking and misalignment.
- Reinforcement—Steel rebar properly positioned and anchored within concrete increases strength, durability, and impact resistance.
- Concrete Mix Design—Balancing strength, workability, permeability, and curing rates ensures quality that withstands freezing, moisture, and sustained use.
- Surface Texturing—Small line texturing creates slip resistance. Patterns, stamps, stains, and etchings can provide visual interest.
- Handrails & Lighting—Handrails aid stability along extended step runs. Creative lighting accents enhance safety and ambiance.
- Sustainability—Permeable concrete, recycled aggregates, and steel alternatives reduce environmental impact.
- Maintainability—Simple maintenance plans prevent major repairs. Easy access for upkeep is key.
How to Lay Out Concrete Steps
Properly laying out concrete steps starts with evaluating the overall intended travel path and slope of the terrain.
Steps should be oriented directly in the direction of foot traffic flow whenever possible. Switchback designs may be necessary to accommodate steeper grade changes. Landings can act as intervals to break up longer runs of steps.
Once the general orientation is determined, the actual sizing of the steps comes next. Concrete steps are defined by three main structural components:
- Treads—The horizontal walking surface of each step
- Risers—The vertical face between each tread
- Nosings—the exposed front edge of the tread
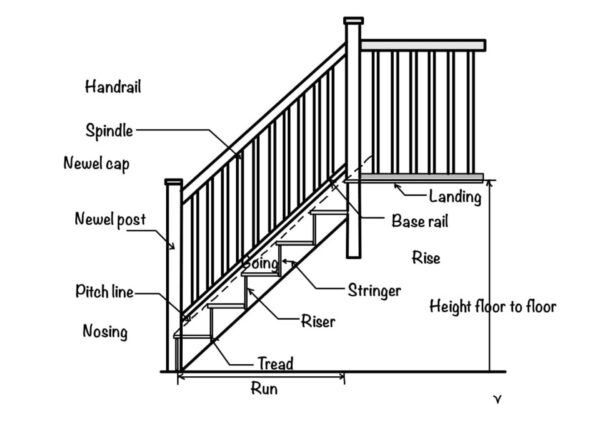
Components of concrete staircase
- Stringers—The structural side supports that hold up the stair treads and risers. Stringers are often concrete but can be wood or steel.
- Treads—The horizontal part of each step that you step on. Concrete treads are typically poured and finished in place.
- Risers are the vertical sections that sit between each stair tread. Concrete risers can be poured or use veneers.
- Landings—The flat resting areas between stair runs. Concrete landings are designed to specific loading requirements.
- Foundation—A reinforced concrete foundation supports the entire stairway load on the ground.
- Railings—Railings provide safety and stability when ascending/descending. Metal railings mount on the concrete.
- Finishes—Exposed concrete stairs can be stained, stamped, or etched to customize aesthetics.
- Joints—Control joints and isolation joints in the concrete prevent cracking from movement/shrinkage.
- Lighting—Integrated lighting on risers or handrails improves visibility and ambiance.
Minimum Thickness of Concrete Steps
Outdoor concrete steps should have a slab thickness between 6” and 8” to withstand loading and environmental factors.
The ground under the steps must be dug out properly, and then 4” to 6” of gravel should be packed down tightly for stability before pouring the concrete.
This provides excellent drainage and frost protection. Added concrete strength or thicker dimensions may be specified in cold climates.
Standard Size of Concrete Steps
The standard dimensions of residential concrete steps are 12” deep treads and 6” to 7” tall risers. Overall step runs match the riser height-to-tread depth ratio for optimal use.
The width spans 36” to 48” based on traffic needs. Wider steps allow convenient two-way traffic and meet accessibility standards. Municipal codes dictate constraints too.
Best Material for Concrete Steps
Concrete offers optimal durability and customization ability for exterior steps.
A compressive strength of 4,000 PSI using Portland cement, sand/gravel aggregate, and a 0.45 w/c ratio produces a frost-resistant concrete mix suitable for steps in most regions. It holds up well to concentrated loads and water absorption while enabling versatile finishes.
Decorative Concrete Steps
Adhesive stone veneers, color treatments, stamping, etching, and stenciling allow for decorative concrete steps with unique visual appeal.
Contrasting riser and tread patterns or integrated lighting create distinctive designs. Textured treads provide better traction. Decorations suit property aesthetics without sacrificing structural performance.
Reinforced Concrete Steps
Steel rebar reinforcement that is correctly placed in concrete step slabs and securely attached to nearby landings makes the structure stronger and able to hold more weight.
This reduces crack formation risk and boosts longevity in cold climates with freeze-thaw cycles. Rebar sizes match specified concrete strength and span parameters.
Conclusion: Best Practices for Concrete Steps
Concrete steps remain a top choice for homes, gardens, and businesses due to their unmatched durability, versatility, and value.
Concrete steps remain the benchmark for exterior durability, safety, and versatility. Pay careful attention to dimensions, reinforcement, surface finish, and drainage.
For best results, use a high-quality concrete mix, reinforce every step, and follow layout guidelines for safe, attractive, and long-lasting outdoor concrete stairs in patios, porches, landscaped pathways, and public buildings.
Plan dimensions around comfort—riser heights of 7 inches, tread depths of 11 inches, and step thicknesses of at least 4 inches.
With the correct design and materials, your outdoor concrete staircase will enhance any entry or garden space for generations.






