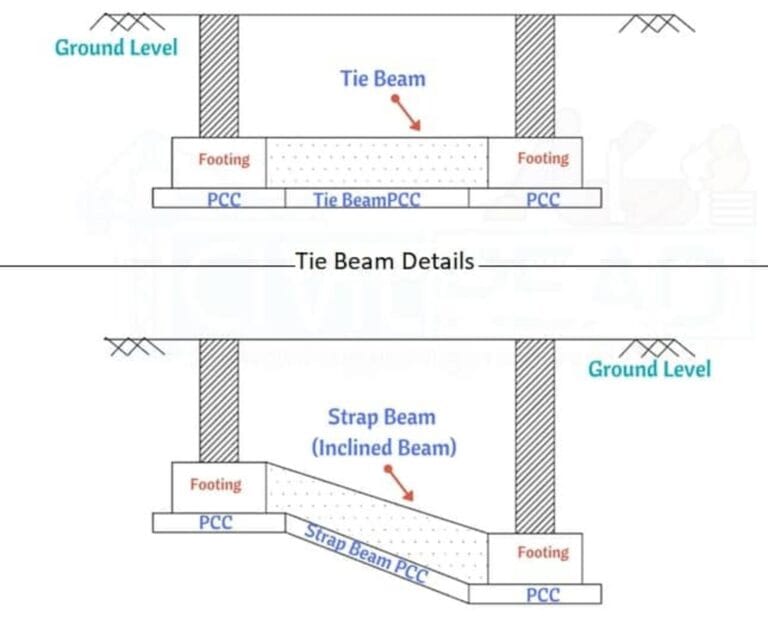
Helical Piers vs. Concrete Footings: Choosing the Right Foundation Solution
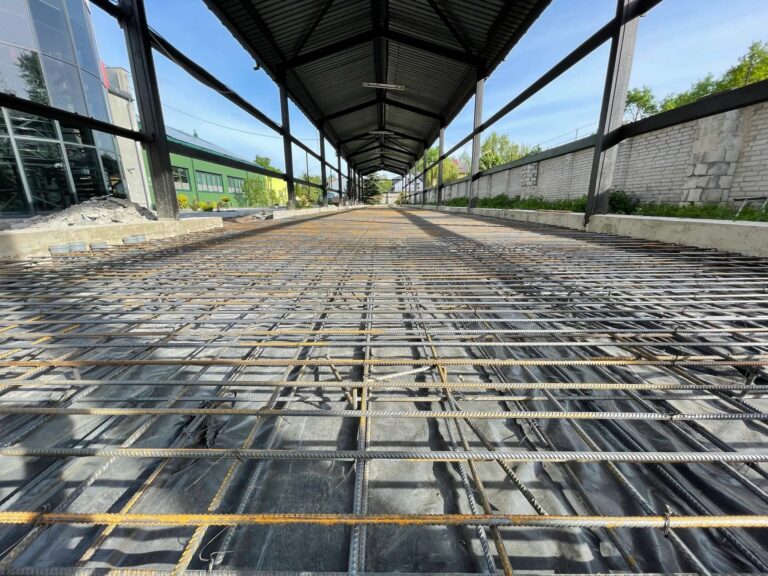
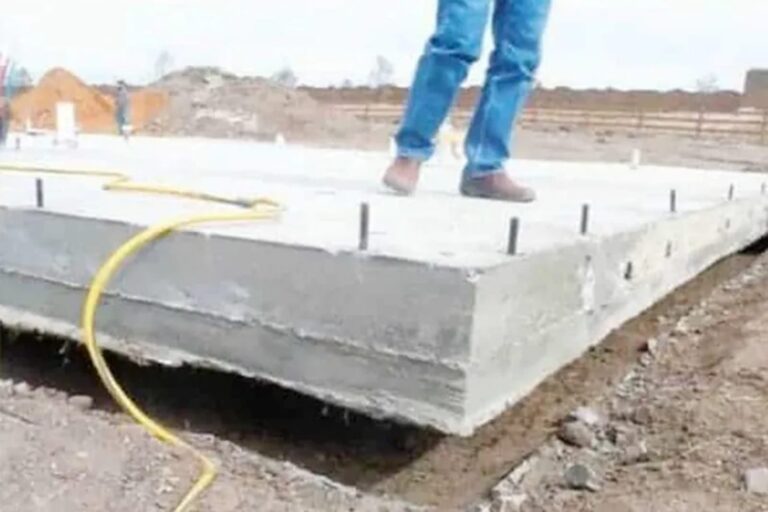
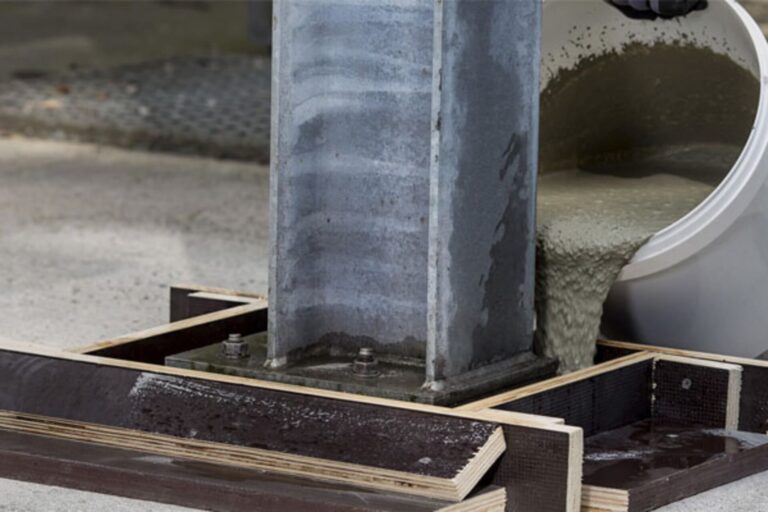
Building a new structure, whether it’s a home, deck, or addition, requires a solid foundation. Two popular options are helical piers and concrete footings.…
Read MoreHelical Piers: A Solid Foundation for Your Deck
When it comes to building a deck, the foundation is crucial for ensuring its stability, durability, and longevity. One of the most effective and…
Read MoreLatest Articles
Don’t miss out on our latest articles
Sign up to receive the latest articles right in your inbox.
email address
*Replace this mock form with your preferred form plugin
Concrete Technology
10 Steps and Types of Slump in Concrete Test
May 31, 2024
Structural Design
Shear Wall Construction: A Comprehensive Guide
June 2, 2024
Grouting Guide
Strength of Materials
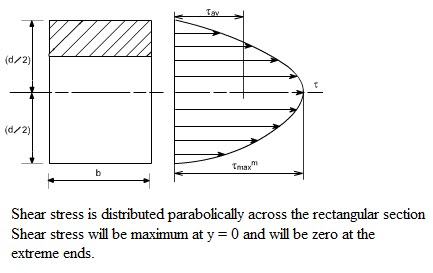
Understanding Shear Strain in Materials
January 30, 2024
Bending Stress in Beams- an engineering guide
January 30, 2024
Reach out for guest article or sponsorship opportunities
Lorem ipsum amet elit morbi dolor tortor. Vivamus eget mollis nostra ullam corper.
Contact Us