- Aggregate crushing value is the measure of resistance of aggregate to crushing against gradually applied compressive load.
- This test is conducted to determine the crushing strength of aggregate.
- This test helps to assess the suitability of aggregates for use in road construction and other applications where they are subjected to high compressive stresses.
- The specifications for this test are given in IS : 2386 Part IV 1963 mechanical properties.
Procedure
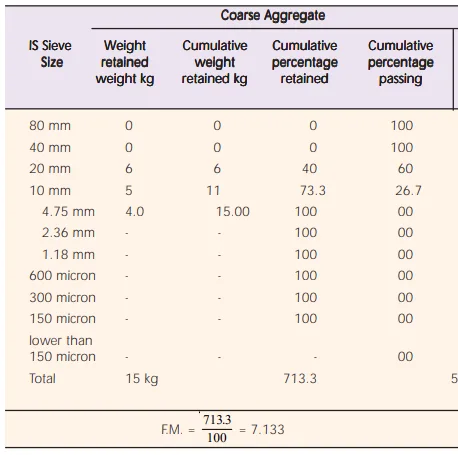
- The material for this test should consist of aggregate passing through 12.5 mm sieve and to be retained on 10 mm sieve.
- About 6.5 kg of sample is placed in the cylinder of the test apparatus and the weight of the material consisting of the test sample is measured as (A).
- The whole setup is placed on a compressive testing machine and these aggregates are subjected to a load of 40 tons.
- The crushed aggregates are removed from the cylinder and are passed through 2.36 mm sieve. The fraction passing through the sieve is measured as (B)
Aggregate crushing value (ACV) = B/A x 100
Where B = weight of aggregate passing through 2.36 mm sieve
A = weight of the surface dry sample taken in mould
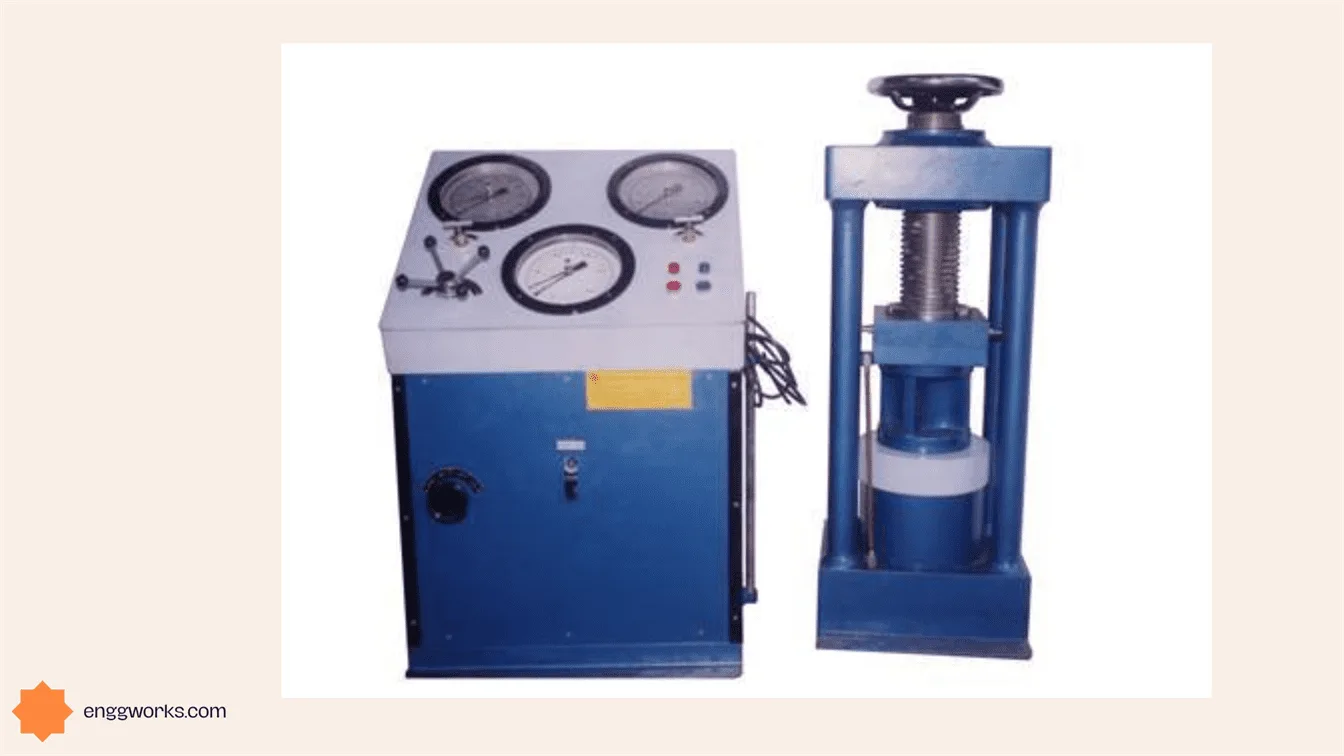

Note
ACV should not be more than 45% for use in concrete other than wearing surfaces, and 30% for concrete used for wearing surfaces such as roads, runways and airfield pavements.Fig