Composites are highly adaptable and can be made use in various applications. As they are robust, stiffer, lighter than metal and moldable to any shape. They can also be tailored to meet required properties of a particular application.
Fiberglass or Glass fiber composites (GFC) are one kind of fiber reinforced composites material with low density, high tensile strength, and easy processing.
So widely used in aerospace, automotive, race vehicles, boats, sporting goods and other industrial applications.
The GFCs strength/weight ratios are higher than those of most other materials and their impact resistance is phenomenal.
Further they possess good electrical properties, resistance to moisture, heat and chemicals and outdoor weathering.
During 1942 glass fiber reinforced composites were first used in structural aerospace parts. In early 1960’s high strength glass fibers, S-Glass were first used in joint work between Owens corning textile products and the US air force.
Later in 1968 S-2 glass began evolving into a variety of commercial applications.
Fiberglass Composite Material properties
Fiberglass composites are artificially produced multiphase materials.
More precisely these are the materials consisting of glass fibers of high strength and modulus embedded in a polymeric matrix with distinct interfaces between them.
Glass fabric is one type of fiber reinforcement. They also come under reinforced polymer composites. Continuous glass fibres are the first type to be used in advanced composites. They are made by pulling molten glass at high temperatures.
Mechanical Properties
- Incombustibility
- Corrosion resistance
- High strength at low densities
- Good thermal.
- Sound insulation
- Special electrical properties.
Types of glass fiber
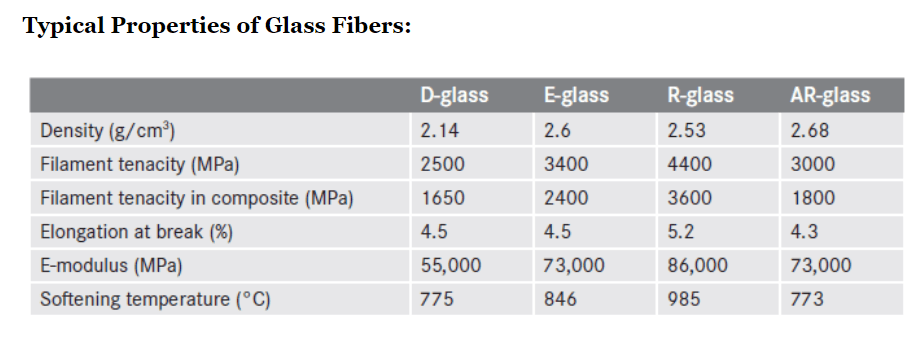
A Soda-lime glass.
E Electrical type (Borosilicate)
C Chemical resistant type
AR Alkali resistant type
S High performance application
Of all soda lime glass is predominantly used for manufacturing a wide array of glass products, including light bulbs, window panes, bottles, and art objects.
It is inexpensive, chemically stable, reasonably hard, and extremely workable, because it is capable of being re-softened a number of times if necessary to finish an article.
Manufacturing of Reinforced glass – s-glass and e-glass
S-glass is a high performance composite, with more silica content. It contains oxides of silicon, aluminum and magnesium. The typical tensile strength properties are 4600 MPa and for E-Glass is 3400 Mpa. e-Glass is also known as electrical glass. The e-glass and s-glass thermal expansion are around 52 and 25.
It is made from the oxides of silicon, magnesium, aluminum, calcium and boron. s-glass and e-glass are mainly used in applications of fiber-reinforced polymer composite. PEI and PPS are used for high-performance composite applications.
Basic manufacturing involves
- Mixing silica, limestone, boric acid and other minor ingredients.
- The mixture is heated until it melts at about 1260oC/2300oF.
- Letting the molten glass flow through fine holes.
- The glass strands are cooled, gathered and wound.
- The fibers are drawn to increase the directional strength.
- The fibers are woven into various forms for use in composites.
Glass fiber reinforced Molding techniques
Most commonly used techniques are :
- Hand and spray saturating and mixing.
- Continuous impregnation, laminating.
- Compression, transfer and injection molding.
- Filament wrapping and winding.
- Centrifugal and static casting.
- Rotational molding.
- Cold forming.
Applications of Glass fiber Composite
GFCs are making inroads many markets due to properties of excellent molded surface finish, almost unlimited size, lightness of weight, insulation against heat transfer and electricity and many other attributes.
Aerospace and aircraft-
These include overhead storage bins, aircraft toilets and helicopter rotor blades. Other benefits from using composites include cost performance, dimensional stability and corrosion resistance.
External fuselages of smaller planes, interior and commercial plane (Boeing 747) entire exterior of flight vehicle guided missiles have been constructed using GFCs.
Construction and Infrastructure-
For rebuilding or creating new infrastructures, composite materials bring a number of benefits including high strength, reduced weight, corrosion resistance, lower maintenance, dimensional stability, good flexural strength, shear strength, low installation costs and design flexibility.
Exterior- In columns, pediments, domes, paneling, cladding, insulation panels, protection coverings, doors, windows, roofing applications and gives an aesthetic look to buildings.
Interior – Blinds against sun or for decoration, ceilings, partitions, furniture, sanitary ware, flooring, decorative items and drywall tapes.
Consumer goods-
Controlled flexibility, high mechanical strength, lightness of weight, easy formability, durability, molded in colors, excellent surface and resistance to corrosion and wear made the GFCs applicable in consumer goods.
They include- furniture frames, divider screens, utility trays, fishing rods, playground equipment, sake boards and surfboards.
Corrosion resistant products-
Engineers have realized that the excellent corrosion resistant property of GFCs made it ideal in various corrosive and hostile environments.
They include all types of pipes, oilfield pipes, fume handling ducts, underground petrol tanks, sucker rods, drainage and irrigation piping (potable water, sewage, storm drains), cooling towers, component for water and sewage treatment facilities, flood control and navigational waterway structures (dam gates, pipes, grating, weirs), energy production structures for oil and gas production (offshore platforms, grating, piping).
Electrical and Electronic-
Mechanical strength and temperature stability were the factors, which favored the use of glass filament technical fabrics in industry as an insulator for electrical conductors.
One such fiber that shows superior thermal insulation property is glass wool as the air trapped in its tiny aip pockets make it a poor conductor of heat.
Other properties include Weather stability, high dielectric strength, high arc resistance and good mechanical toughness.
They are used in distribution-pole hardware, switchgear, and transformers, telephone equipment, PCB’s, computer parts and optical fibers.
Marine accessories-
The major benefits of using GFC’s in any boat construction are moldability to almost any boat design or size, seamless construction, high strength and great durability, minimum maintenance, freedom from corrosion, rust, dry rot and water logging.
About 70% of all outboard pleasure boats are now constructed with GFCs. Small motorcrafts, water sports surf, ski boats, sailboats of all sizes are being fabricated using GFC’s.
Commercial and military hulls including the fishing boats, lighters (LASH) (saving 40 tons per unit compared to steel construction) , submersibles, hovercraft for fast commuter service.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
Why fiberglass composite?
Fiberglass (FRP/GRP) composites offer several advantages over more traditional materials. These advantages include: Cost effective – especially for complex shapes. Corrosion resistant.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of glass fiber composite?
They are transparent, easily formed and most suitable for window glass. But the disadvantage of this glass is its poor resistance to heat (500–600°C).
How do glass fiber composites work?
Glass Fiber-Reinforced Composite (GFRC) is a thermoset plastic resin that is reinforced with glass fibers . Weight, dimensional stability, and heat resistance are given by fiber. Additives provide color, decide the surface finish, and influence many other characteristics, such as wear and flame retardancy.
Glass-reinforced Products
A comprehensive list includes, tooling industry – forming dies for plastic and metals, checking fixture, hydro forming shapes, hammer forms, stretch dies, foundry pattern and many other creative and utilitarian elements.
Green composites are the new trend. These bio-composites are more sustainable and cost less.
Orthopedic casts and prosthetic appliances, in traffic-control signals, in various control instrumentation, in sales-code reading devices and so on.
These applications made fiber glass composite to take away the market over conventional materials like metals.
With new technological advancements in GFCs , they are able to satisfy the needs of particular engineering applications and a solution to many engineering obstructions.
