In our daily life we say loads are nothing but the weights that act on a body or a material. That exerts the pressure or stresses on it. Live load vs dead load discussion will give the full meaning. They are something that are considered very important in civil engineering. They play a crucial role in the construction process.
A building or a structure is subjected to various forces that act on it throughout its lifetime. These forces cause stress, deformations , displacements or deformations on the structure are called loads or structural loads.
The loads acting on a structure are an important consideration in structural design. Building codes provide the limits for maximum and minimum loads that a structure can resist during its service life . These values depend on the type of structure, building materials used, geographic location etc.
In civil engineering, total dead and other loads are applied to a structure. It should not exceed the permissible stresses. The moving loads are different. The life of the structure depends on how the structural elements are arranged and loads carried by it.
Generally the structural loads are categorized into different types based on their origin as gravity or vertical loads, horizontal and longitudinal loads.
Live Load vs Dead Load – Structural Loads and Environmental Loads
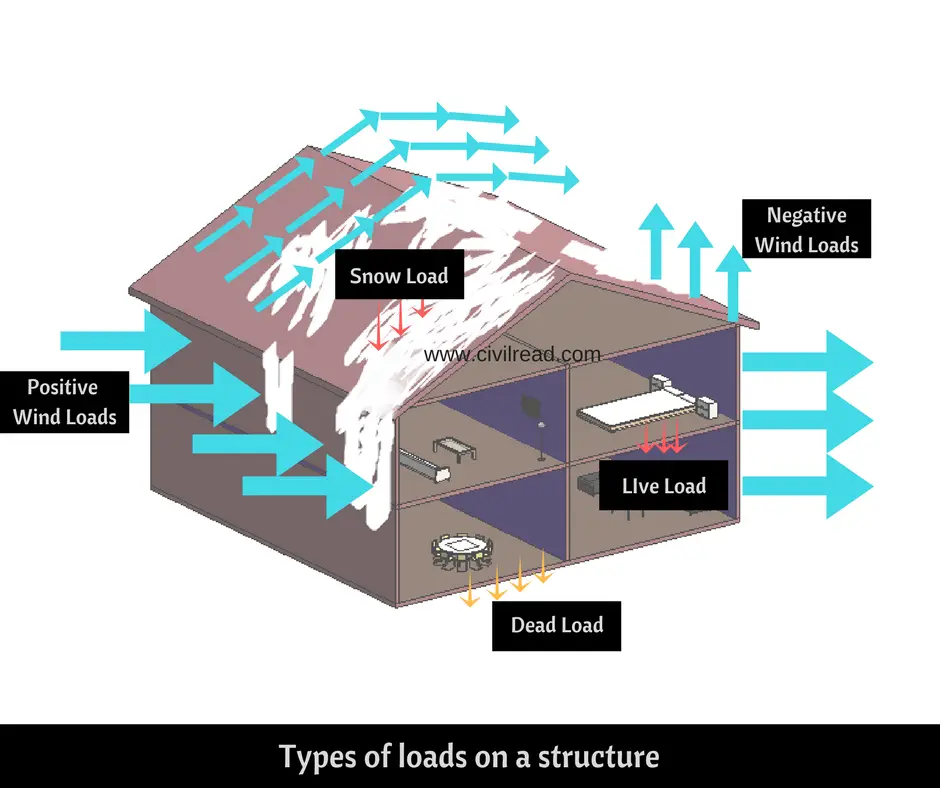
The total load acting on a structure is basically categorized as dead load and live load. Both are the same gravity loads acting on a structure in the vertical direction but are different in exerting the stresses on the structure.
Dead load is a permanent and static load whereas live load is temporary and dynamic in nature. Dead load is constant over time and live load keeps on changing over time. Both the load calculations are different and are carried out following their codes respectively.
Loads may vary based on temperature and other conditions. Total dead plus live loads are used in assessing structural strength of the member. The weight of the structure is a dead load. Live loads are usually dynamic.
The dead and live load combination are used in calculation of length, depth of column and beams. Building’s life span is dependent on the different design criterion.
Live load requirements vary for a truss compared to a dam. Loads on a structure have to be calculated carefully. Load per meter, or area are used in design.
The anticipated live loads should be scientific in calculation. The minimum design load types should be capable to withstand all weight of people and change over the life.
The dead load should not exceed a percentage of the maximum anticipated live load. Live loads in multi-story buildings vary based on swimming pools, antennas, goods etc. The loads in your design of structures should meet the code guidelines.
Part of the building may carry more live load, which can be changed to uniformly distributed live load. Examples of live loads vary based on structure. In the design of a structure, occupancy and intended use should also be known.
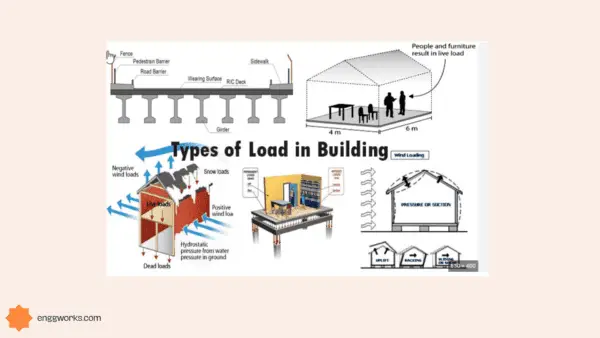
Types of loads in Structural Design
Vertical Loads
- Dead Loads
- Live Loads
- Snow Load
Horizontal Loads
- Wind Load
- Earthquake or seismic Loads
In this article we will discuss in detail the live load vs dead load, their importance in structural design, and differences.
Dead loads in Civil Engineering
A gravity or vertical load that is permanent, static and constant and remains the same throughout the life of the building is called a dead load. These static loads transfer the load to the structure. It is also known as permanent or static load.
Dead loads in structural design are calculated as force per area. Most of these are permanent or static loads.
Generally the dead loads or the permanent loads refers to the self-weight of the structure itself which remains constant over time period.
It also includes the immovable fixtures such as the weight of the concrete slab, walls, flooring etc. They can be considered as the load acting uniformly over the entire structure.
Dead loads calculation plays a very important role in designing a building, its durability . failing to do the accurate calculation may result in collapse of the structure. The magnitude of dead loads can be calculated by knowing the unit weight of materials used.
Using the code IS 875(part 1):1987 Indian Standard Code of Practice For Design Loads (Other Than Earthquake) For Buildings And Structures- Dead Loads – Unit Weights Of Building Materials And Stored Materials, can be calculated.
Units considered in calculation of dead loads are KN.
Live load using Building Codes
These are something different from dead loads. Live loads otherwise called as imposed loads are vertical or gravity loads that are defined as the moving or movable loads which are not constant but keep on varying over the time period. These are temporary loads and are dynamic in nature.
Live loads refer to things like furniture, people, cars, trucks, buses, water etc which keep on changing.
The movable objects can be considered as live load. The intended use of a building or dam or canal, is to carry these loads. In some important structures the seismic activity is also considered.
These dynamic loads include the moving partitions, objects, equipment, people, vehicles etc. roof and floor live loads are also produced during the maintenance works. Usually the live loads are considered as uniformly distributed loads or sometimes concentrated loads. It is generally specified in the IS: 875-1987(PART 2) code depending on the type of building and type of load imposed.

Loads are usually carried by beams, columns, slab and footing in a normal building. Extreme snow can also increase load on a roof. The weight of its components can act vertically or horizontally. Loads account for the major stresses.
Live loads are categorised into different types based on their origin such as
- Floor load
- Roof load
- Imposed loads(people,furniture etc)
- Staircase load
- Balcony load
- Movable fixtures etc.
Units of live load are taken as pounds per square foot (psf) , kPa, N/m2, kg/m2.
Environmental loads
These are the forces or the pressures that nature puts on the buildings due to some atmospheric conditions and environmental factors like wind, snow, rain, earthquakes, soil conditions and varying temperatures.
These loads affect the durability and integrity of the structure if the structure is not properly designed to withstand such conditions. Therefore it is necessary to include or consider the environmental loads in design and construction of the buildings. However engineers use the building codes in their designs for accounting these loads according to the local environmental conditions.
Design should always exceed the estimated stress. A particular structural element has to withstand wind force or too much “gravity load or actual load. The maximum expected live load is based on experiments and from surrounding buildings. Permanent force on a structure should be less.
Some common types of environmental loads are
- Wind load
- Snow load
- Seismic or earthquake load
- Temperature load