Composite materials have played a predominant role throughout human lives.
From early civilization to enabling future innovations.
A composite is a material obtained by amalgamation of two or more distinct materials to achieve a material with enhanced properties compared to the parent materials.
These two or more different materials are quite dissimilar in toughness, compression and in their properties. They don’t mix or blend with each other.
They work together to enhance the composite with unique properties.
Composites exist in nature, few include wood, bone, stones etc.
These are natural composites either grown in nature or developed by natural process.
Wood is a composite with its long cellulose fibers held together by a lignin substance. They do not follow the rule of mixtures.

Need for composite materials
Composites penetrated into human lives for the past many years.
Almost every material we see around is made of composite.
Such as products used in constructions, transportation, aviation, sports and many more.
The need for development of composite material is due to its unique properties superior to component materials.
The first and foremost one is light weight which is very crucial in applications of aerospace and automobile industries.
The other include corrosion resistant, high strength, stiffness.
Many composites can be customized to attain desired material properties like good conductors or insulators of heat or certain magnetic properties.
There are wide range applications in manufacturing of electrical devices.
For example transistors, diodes, sensors, detectors and to make anti surface coatings anti corrosive coatings.
Composites made of metal oxides have specific electrical properties used in making silicon chips that improves the memory and speed of the computers.

Different materials like glass fiber, fiber reinforced composites are all made from the composite structure.
Individual materials having different chemical or physical properties are combined together and composite materials are created.
The lightness of composite materials made, makes it use in different industries. Mixture is different from composite products.
Making of Composite Material
Many of the composites are obtained by merging two materials of which one is matrix (fiber) and the other one is reinforcement.
These composites are called fiber reinforced polymers (FRP).
An example of FRP is fiberglass in which the fibers or threads of glass are the reinforcement and the matrix is plastic.
The glass thus obtained is of high strength and is light in weight, which is advantageous in many applications.
In general composites have three components.
- The matrix, continuous phase.
- Reinforcement, discontinuous or dispersed phase includes fibers and particles
- The fine interface region.
By carefully selecting the matrix, reinforcement and manufacturing technique. An engineer can customize certain properties to meet the requirement of the application.
Matrix selection
Any material can serve as a matrix in composite material.
Generally used matrices are metals, polymers and ceramics.
The matrix composite has different physical properties and mechanical properties.
Majorly used matrix material in composites is polymer.
There are different types of polymers of which thermosetting and thermoplastic polymers are widely used.
Among them thermoset is most predominantly used compared to thermoplastic.
Though both thermoset and thermoplastic sound the same.
They have different properties and applications.
Understanding their performance helps in designing the composite.
The strength and stiffness also vary based on the constituent material used.
Fiber reinforcement is used in boat hulls to make it strong.
Material made of reinforced composite can be used in aerospace applications.
Polymer matrix can easily bend and used in biotechnology and resist cracks and fractures.
Resistance to corrosion is another advantage.
Compared to metal fibers, glass fiber and polyester are used in civil engineering.
Two or more materials can be clubbed together.
The properties of the composite need to be tested in the lab. Core materials have some deficiencies.
Thermoset
Thermoset are the materials in liquid form and strengthens and becomes hard when cured or heated.
Once heated thermosets can be molded, shaped and pressed.
The setting process is irreversible.
This means they are permanently set and have high strength and do not melt or soften when exposed to high temperatures.
Epoxy is one example. The plastics can withstand wear, corrosion attacks under extreme environments.
Thermoplastic
Thermoplastics are hard at low temperatures and become soft when heated to their melting point.
These materials are reversible as they solidify once the heat source is removed and the temperature is dropped below its melting point.
Examples include ceramics, metals and carbon.
Reinforcement
Composite reinforcement can be in particle, flakes or fiber form.
Each of these has its own properties. That contribute to composites and each has their own area of application.
Among them fiber form is more predominant in use as it has the most influence on composite properties.
Various types of fibers are used to reinforce, most commonly used are glass fibers , carbon fibers, boron fibers.
Fibre reinforcement can be used in aeronautical industry and for swimming pool.
Composite includes reinforced plastics and materials with high strength to density ratio.
Manufacturing techniques – Properties of Composites
There are several methods for fabrication of composite materials.
Selection of the method depends on the material, part design and application.
Usually the basic method involves the intrusion of reinforcement material into the mold.
Then spraying the semi-liquid matrix to form the object.
Now pressure may be applied to remove air bubbles and finally subjected to heat to make the matrix set solid.
This is called the Pultration method and done by hand or machine.
This can be done for objects with uniform cross -section and are straight like bridge beams .
Many other processes are evolved for parts with various cross-sections, complex shapes, curved panels, thin structures and for certain applications.
These techniques can be further explained in detail by the following methods-
- Open hand moulding
- Resin intrusion moulding
- Automated fiber placement
- Additive manufacturing
- Filament winding
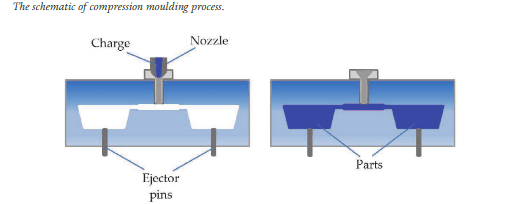
- Injection moulding
Sandwich is another composite making technique in which matrix reinforcement is not used.
In this multiple layers of the materials. The structure of this type of composites consists of a honey-comb layer of plastic.
Sandwiched between two skin of carbon-fiber composite.
These sandwich composites have high strength, bending stiffness and light weight.
Frequently Answered Questions (FAQ) – Composite Materials
What are composite materials?
Composite materials are materials made by combining two or more different types of materials to create a new material with improved properties. These materials are designed to harness the strengths of individual components while minimizing their weaknesses. Common examples of composite materials include fiberglass, carbon fiber, and reinforced concrete.
What are the advantages of using composite materials?
Composite materials offer several advantages over traditional materials in various applications. They are known for their high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent durability, and resistance to corrosion. Moreover, composites can be tailored to specific requirements, allowing engineers to optimize their performance for a wide range of applications.
What are the different types of composite materials?
Composite materials can be classified into several categories based on their matrix and reinforcement materials. Some common types of composites include polymer matrix composites (PMCs), metal matrix composites (MMCs), and ceramic matrix composites (CMCs). Each type has unique properties and is suitable for specific applications.
How are composite materials manufactured?
Composite materials are manufactured using different techniques depending on the type and application. Some common manufacturing methods include layup, filament winding, pultrusion, and injection molding. These techniques involve combining the matrix and reinforcement materials, shaping the composite, and curing it to achieve the desired properties.
What are the applications of composite materials?
Composite materials find applications in various industries due to their unique properties. They are extensively used in aerospace and automotive industries to reduce weight and improve fuel efficiency. Composites are also used in construction, sports equipment, marine structures, and renewable energy systems, among others.
Composite Material – Applications
Benefits – composites offer many benefits such as- corrosion resistance, low density, low material cost, durability, design flexibility, improved productivity, strength.
Applications – considering the range of benefits, composites are widely used in various industries. Some of the common applications include
Aerospace- rotor shafts, radar, jet engines, flywheels , turbine blades, turbine shafts, transmission structures, compressor blades, wing box etc
- Transportation and automobile industry
- Construction and infrastructure industry
- Corrosive environment
- Marine sports
Even though the composite has a wide range of applications.
The manufacturing process is easy and efficient with composites.
The downside of it is cost. The cost of the raw material is high.
Composites have long service life with little maintenance, and can withstand harsh environments.
Composites with all its advantages and benefits can never replace traditional materials.
Like steel but can serve the purpose that we need.
With further advancements in research there is no doubt that composites will have a wider range of applications.