One important ground improvement technique among such is grouting.
Grouting plays a very major role in improving the strength , durability and safety of the structures in the construction process. It has several advantages in various aspects of engineering such as waterproofing, soil stabilization, tunnelling , removal of honeycombing etc.
There are different types of grouting techniques used depending on the requirement of the project , soil, material characteristics etc.
What is soil stabilization?
Soil stabilization is the process of improving the soil properties such as increasing its bearing capacity, stability, strength etc by applying some of the ground improvement techniques such as soil compaction, preloading of soil, piling etc. It can be achieved by modifying the physical, chemical or biological properties of the soil.
In this blog post, we will explain how pressure grouting works and what are its benefits in soil stabilization.
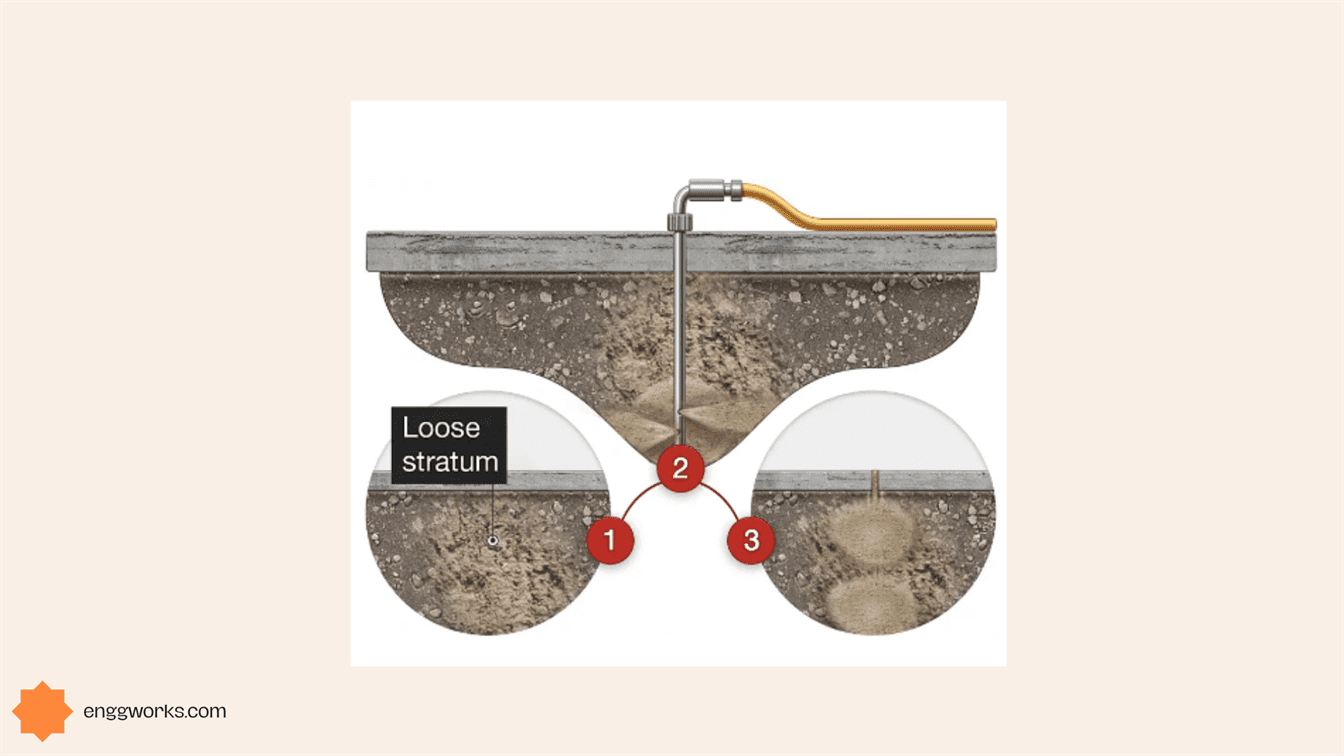
Pressure grouting soil stabilization
Pressure grouting is a technique that improves the soil properties by injecting a fluid grout into the soil to improve its strength and stability under controlled pressure.
It can be used for various applications, such as foundation repair, slope stabilization, tunnel sealing, soil compaction such as ground improvement, compensation for ground settlement, and reinforcement of soil nails.
There are different types of pressure grouting methods depending on soil type, grout material used, mode of application etc. Some among them are permeation grouting, jet grouting, compaction grouting and fracture grouting. Each method has its own advantages and drawbacks.
Pressure grouting for soil stabilization involves pumping a cement or chemical grout into soft or weak strata of soil or voids.
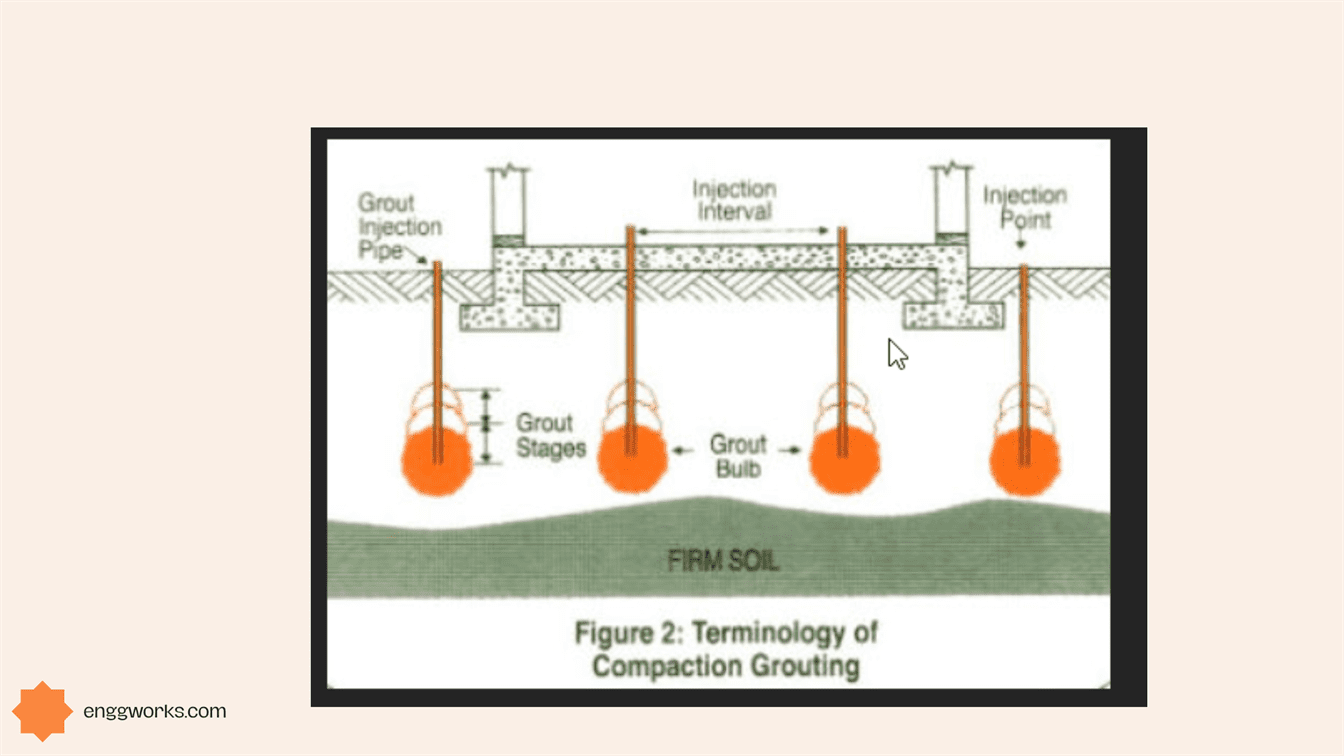
This grout fills these voids, thus stabilizing and strengthening the soil. The grout can be pressurized into the soil through holes or pipes drilled, jetted, or driven to the desired location.
The grouting pressure can affect the efficiency and safety of the process, as well as the characteristics of the grout bulb created underground.
Uses of Pressure Grouting for Soil Stabilization
It has many applications in civil engineering and construction projects. For example, it can be used to support existing structures or where foundations have shifted, to control the ground settlement caused by underground construction or deep excavation, to densify the soil to improve its characteristics, and to enhance the pull-out resistance of grouted soil nails.

It is a cost-effective and versatile technique that can solve many geotechnical problems. However, it requires careful planning and execution to achieve optimal results.
Some factors that need to be considered are the type and properties of the soil, the type and properties of the grout, the method and pressure of injection, the location and spacing of injection points, and the monitoring and quality control of the process.




