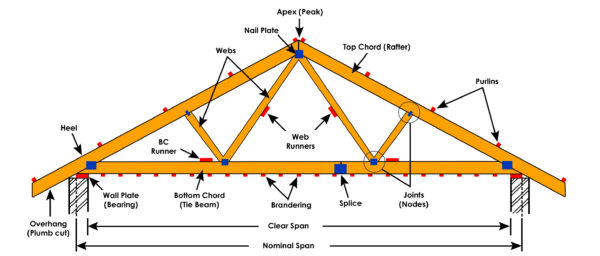
A building layout refers to the arrangement and organization of spaces, rooms, and facilities within a building.
It is a crucial aspect of architectural design that determines how people will navigate, interact, and utilize the built environment. A well-designed building layout ensures functionality, efficiency, and comfort for its occupants.
Purpose of Building Layout
The primary purpose is to create a functional and efficient space that meets the specific needs of its occupants.
It aims to optimize the use of available space, facilitate smooth movement, and ensure the safety and well-being of the people using the building. A well-planned layout also contributes to energy efficiency, accessibility, and the overall aesthetics of the building.
principles of building layout
Here’s a sample plan that demonstrates the principles discussed in the blog post:
+-----------+-------------------+------------+
| | | |
| Private | | Meeting |
| Office | Open Office | Room |
| | | |
+-----+-----+-------------------+------------+
| |
| |
+-----+------------------------------------+-+
| | | |
| Private | Collaboration | Break |
| Office | Area | Room |
| | | |
+-----------+-------------------+------------+
|
|
+------+-------+
| |
| Reception |
| |
+-------------+
|
|
+-------+--------+
| |
| Entrance |
| |
+----------------+This plan incorporates several key principles:
- Zoning: The layout is divided into distinct zones based on function – private offices, open office area, collaboration space, meeting room, break room, and reception.
- Open office: A large, open office area promotes collaboration and flexibility, with minimal walls and partitions.
- Collaboration spaces: A dedicated collaboration area is included for informal meetings and brainstorming sessions.
- Efficient circulation: The layout provides clear and intuitive pathways, with the reception area located near the entrance and leading to the main workspace.
- Accessibility: The layout ensures that all spaces are easily accessible, with wide corridors and no obstacles hindering movement.
- Shared resources: Common facilities like the break room and meeting room are centrally located to be easily accessible from all parts of the office.
- Flexibility: The open office area and collaboration space can be easily reconfigured to accommodate changes in team size and work styles.
This sample layout demonstrates how the principles discussed in the blog post can be applied to create a functional, efficient, and comfortable office space that meets the needs of its occupants.
Building Layout Design Ideas
When designing , consider the following ideas:
Open floor plans: Promote collaboration and flexibility by minimizing walls and partitions.
Modular design: Use standardized units that can be easily reconfigured to adapt to changing needs.
Natural light and ventilation: Incorporate windows and skylights to reduce energy consumption and improve indoor air quality.
Efficient circulation: Design clear and intuitive pathways to facilitate movement and reduce congestion.
Building Layout Plan Examples
Here are some common examples of building layout plans used in civil engineering and architecture:
Office Building
- Linear layout with a central corridor and offices on either side
- Open plan layout with collaborative workspaces and breakout areas
- Modular layout with flexible partitions and adaptable spaces
Residential Building
- Apartment layout with efficient use of space and clear zoning
- Single-family home layout with open-concept living areas and private bedrooms
- Townhouse layout with vertical stacking and shared walls
Commercial Building
- Retail store layout with strategic product placement and customer flow
- Restaurant layout with efficient kitchen design and seating arrangements
- Supermarket layout with organized aisles and checkout counters
Industrial Building
- Factory layout with optimized production lines and material handling
- Warehouse layout with efficient storage and retrieval systems
- Distribution center layout with streamlined loading and unloading areas
Educational Building
- School layout with classrooms, laboratories, and common areas
- University campus layout with academic buildings, libraries, and student housing
- Training center layout with workshops, seminar rooms, and simulation labs
Healthcare Building
- Hospital layout with patient rooms, operating theaters, and diagnostic facilities
- Clinic layout with examination rooms, waiting areas, and administrative offices
- Nursing home layout with residential units, common spaces, and medical facilities
Recreational Building
- Gym layout with exercise equipment, group fitness studios, and locker rooms
- Museum layout with exhibit halls, galleries, and visitor amenities
- Theater layout with auditorium seating, stage, and backstage areas
These examples demonstrate the variety of building layouts used in different sectors, each designed to meet specific functional requirements and user needs. By studying and adapting these layouts, civil engineers and architects can create efficient, effective, and user-friendly buildings.
Building Layout Considerations
Office Building
When designing an office building , consider the following best practices:
Zoning: Group similar functions together to improve efficiency and reduce noise.
Flexibility: Use modular furniture and movable walls to accommodate changes in team size and work styles.
Collaboration spaces: Include areas for informal meetings and brainstorming sessions.
Ergonomics: Ensure that workstations are comfortable and adjustable to reduce physical strain.
Commercial Building
For commercial building keep these considerations in mind:
Customer flow: Design a layout that guides customers through the space and encourages purchases.
Product placement: Strategically place high-demand items and promotions to maximize visibility.
Security: Incorporate measures such as clear sightlines and secure storage areas to prevent theft.
Accessibility: Ensure that the layout accommodates people with disabilities and complies with ADA guidelines.
Efficient Building Layout Strategies
To create an efficient building layout, employ these strategies:
- Space optimization: Maximize the use of vertical space and minimize underutilized areas.
- Modular design: Use standardized components and dimensions to simplify construction and maintenance.
- Multipurpose spaces: Design rooms that can serve multiple functions to increase flexibility and utilization.
- Technology integration: Incorporate smart building systems to monitor and optimize energy consumption.
Building Layout for Optimal Space Utilization
To achieve optimal space utilization , consider the following:
- Functional zoning: Group related activities together to minimize travel distances and improve efficiency.
- Flexible workspaces: Use adaptable furniture and partitions to accommodate different work modes and team sizes.
- Shared resources: Centralize common facilities such as printers and break rooms to reduce duplication.
- Storage solutions: Incorporate built-in storage and vertical space to maximize usable area.
Building Layout and Fire Safety Regulations
When designing a building layout, ensure compliance with fire safety regulations:
- Fire exits: Provide clear and unobstructed paths to emergency exits.
- Fire compartments: Divide the building into fire-resistant compartments to contain the spread of fire.
- Fire suppression systems: Include sprinklers, fire extinguishers, and smoke detectors in the layout.
- Evacuation plans: Develop and communicate clear evacuation procedures to all occupants.
Residential Building Layout Trends
Current residential building layout trends include:
- Open-concept living: Combine living, dining, and kitchen areas into a single, fluid space.
- Flexible bedrooms: Design bedrooms that can easily be converted into home offices or fitness areas.
- Outdoor integration: Incorporate large windows, sliding doors, and balconies to blur the line between indoor and outdoor spaces.
- Smart home features: Integrate technology for automated lighting, temperature control, and security.
Building Layout and Energy Efficiency
To improve energy efficiency through design:
- Passive solar design: Orient the building and windows to maximize natural light and heat gain.
- Thermal zoning: Group spaces with similar temperature requirements together to optimize HVAC performance.
- Insulation: Use high-quality insulation materials to minimize heat transfer through walls, roofs, and floors.
- Daylighting: Incorporate skylights and light shelves to reduce the need for artificial lighting.
Building Layout and Accessibility Guidelines
To ensure accessibility follow these guidelines:
- Barrier-free design: Eliminate steps, narrow doorways, and other obstacles that hinder movement.
- Clear circulation: Provide wide, unobstructed corridors and pathways for easy navigation.
- Accessible amenities: Ensure that restrooms, drinking fountains, and other facilities are usable by people with disabilities.
- Signage: Include clear and visible signage to guide people through the building.
Conclusion
What are some innovative trends in building layout design?
Innovative trends in building layout design include open-concept living, flexible and adaptable spaces, outdoor integration, and smart home features that enhance functionality and user experience.
What are some common building layout software tools?
Common building layout software tools include AutoCAD, Revit, SketchUp, and ArchiCAD, which allow designers to create, visualize, and modify building layouts digitally.
What is the importance of zoning in a building layout?
Zoning involves grouping similar functions or activities together within a building to improve efficiency, minimize travel distances, and reduce noise and distractions.
A well-designed building layout is essential for creating functional, efficient, and comfortable spaces that meet the needs of their occupants.
By considering factors such as space utilization, fire safety, energy efficiency, and accessibility, civil engineers and architects can develop layouts that optimize the built environment.
Incorporating modern design trends, best practices, and regulatory requirements ensures that buildings are not only safe and sustainable but also adaptable to the evolving needs of their users.