A wall forms an integral part of any building or structural formwork. Walls serve varied purposes including bearing structural loads; separating interior spaces; providing weatherproofing, fire resistance or acoustic insulation; and forming secure perimeters. Choosing suitable wall types and construction techniques based on precise usage requirements is vital in building design.
This comprehensive guide classifies different wall types used in construction and elaborates their structural behaviour, materials, configurations, applications and integration methods in modern infrastructure.
Classification of Walls
Walls can be categorized based on functional attributes:
Load Bearing Walls
As the name suggests, load bearing walls transfer vertical loads from slabs, beams and other structural members safely into foundations. They may support:
- Dead loads like a building’s self-weight
- Imposed loads like furnishings, occupants and storage
- Wind or seismic lateral loads
Based on material and composition, following are key load bearing wall types:
- Concrete – Reinforced concrete, precast concrete panels etc.
- Masonry – Brick, concrete block, stone etc.
- Timber – Heavy timber, laminated veneer lumber etc.
Non-Load Bearing Walls
Non-load bearing walls are built between columns or load bearing elements. They carry their self-weight but no superimposed structural loads. Materials used include:
- Light steel framing
- Timber stud framing
- Metal/wooden partition systems
Retaining Walls
Constructed between drastically uneven ground levels, retaining walls resist lateral earth pressure and provide stabilization. Types include:
- Gravity walls – Rely on self-weight to resist sliding and overturning
- Piling walls – Frictional resistance of vertical piles embedded in soil provides stability
- Cantilever walls – Reinforced concrete stem walls fixed at base

Shear Walls
Designed to counter horizontal forces in a building, shear walls carry loads laterally into connected structural members. Materials range from timber to reinforced concrete.
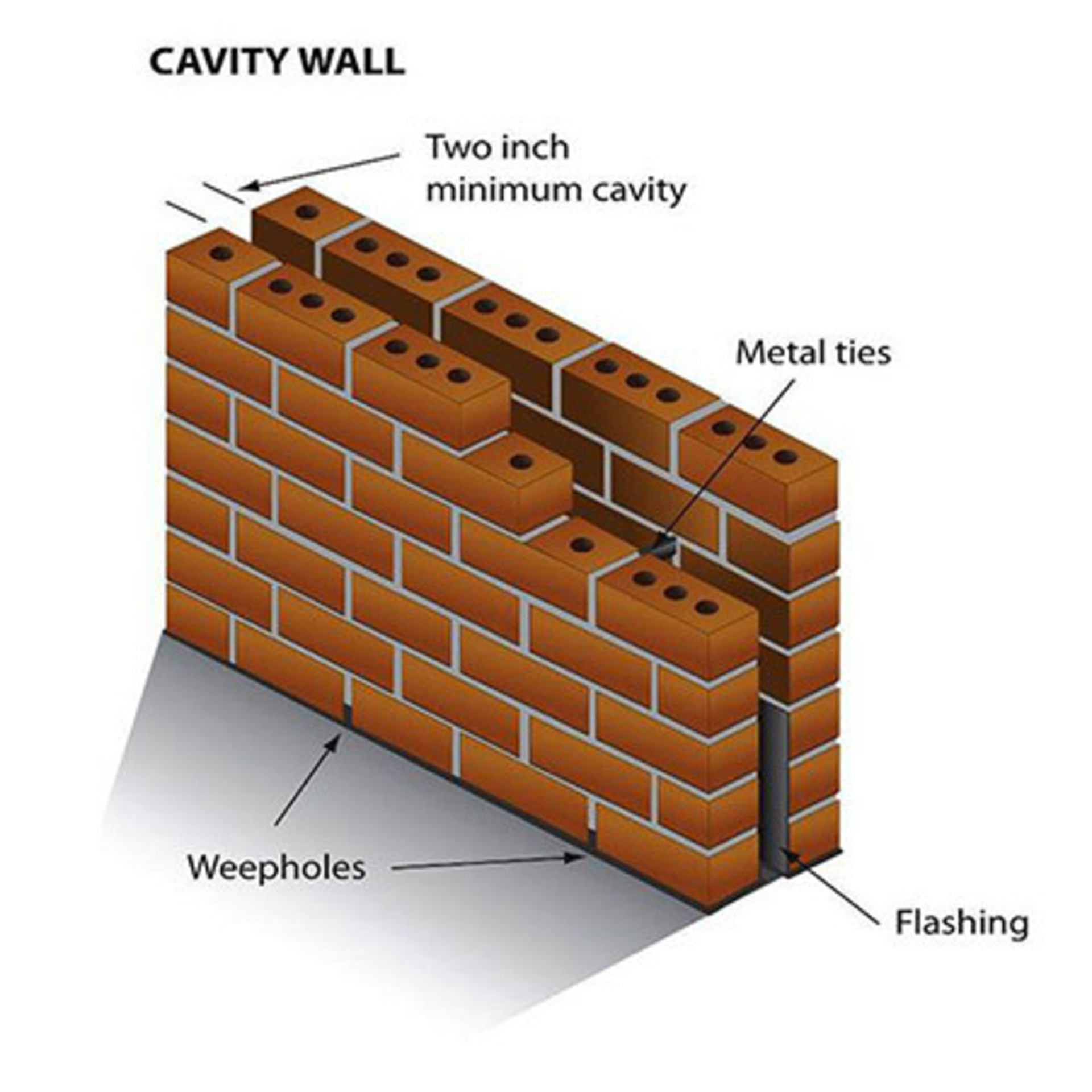
Cavity Walls
Hollow double-wythe construction with external masonry wythe, internal masonry wythe and a cavity between them. Cavity walls prevent moisture ingress efficiently.
Curtain Walls
A non-structural enclosure spanning multiple floors covering the external/internal face of a building as a single, continuous unit. Comprises of glass, aluminum etc. held by vertical and horizontal structural members.
Now that we have outlined major wall types based on structural performance, let’s delve deeper into their configurations, construction methods and usage across residential and commercial settings.
Different Types of Walls Used in Building Construction
Wall construction forms an early stage in any construction project. Several conventional and modern wall types suit varied usage scenarios.
Load Bearing Masonry Walls
Predominant since ancient times, masonry load bearing walls use brick, block, stone or concrete units bedded in mortar and arranged in patterns like English Bond, Flemish Bond etc. Based on material, types include:
- Brick masonry – Solid clay bricks or fly ash clay bricks in cement mortar
- Concrete block masonry – Premix concrete blocks bedded in mortar
- Stone masonry – Dressed stone blocks laid in cement mortar
- Glass block masonry – Glass blocks arranged with open or closed cavities
Masonry bearing walls suit low-rise buildings up to 2-3 storeys. Reinforced masonry introduces steel rebars for additional strength.
Benefits include durability, fire/noise resistance, availability, and aesthetic appeal. However, they require heavy foundations, are labour intensive, prone to dampness issues and building movements.
Pre-Fabricated Concrete Walls
Pre-cast solid/hollow concrete walls are factory manufactured to standard sizes using accelarated curing techniques and transported readymade to site. They offer merits including quality control, speedy construction, simultaneous site preparations and slender profiles compared to in-situ walls.
They are adopted in residential and commercial structures as exterior walls or room dividing walls. Insulated concrete forms (ICF) integrate insulation and enable concrete placement between polystyrene foam forms to give insulated monolithic concrete walls post hardening.
Timber Frame Walls
A traditional skeleton wall construction where the timbers act as structural studs nailed or bolted to horizontal sole plates and cap plates. Used since medieval ages, lightweight wooden frame walls with brick/stone infill suit multi-level buildings.
Modern forms include balloon and platform timber framing fixed using plywood/gypsum boards. They are easy to construct, modify, insulate and install wiring/piping without chipping.
Structural insulated panels (SIPs) fuse wooden or cement boards sandwiching a foam insulation core giving prefabricated, monolithic wall zones.
Steel Frame Walls
Light gauge galvanized steel frames fixed using nuts/bolts comprise vertical steel studs spaced 16-24 inch apart connected by horizontal tracks top and bottom. Depending on loads, steel thickness ranges 0.5mm-0.8mm.
Framing is then lined with finishing materials on either side like plasterboards. Benefits are quick construction, resistance to rot/pests/mold and integration of service lines.
Intermediate Partition Walls
Non-load bearing interior walls dividing living spaces aid privacy, temperature control and noise reduction. They comprise a frame infilled with materials like plywood, particle boards, gypsum boards, glass, blockwork etc.
Wood partition walls use metallic studs or wooden frames where boards are nailed to both sides.
Drywall partitions involve aluminum tracks securing gypsum drywall panels on both sides. No mortar is used diminishing moisture issues. They are easy to install but limited fire resistance.
Glass partition walls create translucent divisions using tempered glass panels secured in hardwood frames or using stancheons. They elegantly admit light.
External Curtain Wall Systems
Floor-to-ceiling external enclosures spanning the building facades made using glass/metal panels integrated into structural aluminum profiles give modern, minimalist exteriors allowing extensive use of glass, protection from weather and high safety from strong winds.
Structural sealant glazing gives ultra-sleek glass facades with vertical/horizontal aluminum members fused using durable silicone sealant without caps/screws. Unitized systems allow pre-assembled curtain wall units to be integrated on-site diminishing construction timelines.
Thickness Considerations for Different Wall Types
The thickness and finishes used for any wall depend chiefly on:
Structural Stability
- For load-bearing walls including external walls, higher thickness from 200-300mm ensures sufficient load transfer and shear resistance
- For internal non-load bearing partition walls, a thickness from 75-100 mm proves adequate
Acoustic and Thermal Insulation
- Hollow cellular concrete block walls from 190-300 mm give better heat/sound insulation
- For wooden partitions, doubling gypsum boards enhances acoustic privacy
Durability Requirements
- For lower superstructure walls exposed to rain or underground retaining walls prone to moisture ingress and chemical attacks, thicker walls from 300-600 mm are resilient
Let us examine suitable thickness standards as per walling material and usage:
- Brick external walls – 230 mm or 340 mm including internal/external plaster
- Brick partition walls – Half brick or 115 mm; single brick or 230 mm
- Concrete block basement walls – 200-600 mm
- Timber stud partition walls – 100 mm
- Drywall partitions – 92 mm (typically 75 mm stud framing with 2 layers 12.7 mm gypsum boards)
- Glass partitions – 15-25 mm thick monolithic tempered glass
Freely combining distinct wall types creates interesting articulations tailored to functional zones. For instance, glass curtain façades for the office lobby, brick bearing walls for the lecture hall block and lightweight drywalls/partitions for the administration wing – all integrated coherently!
Construction Methods, Materials and Fastening Systems
Let’s outline the stepwise procedures involved in constructing different walling systems:
Brick/Masonry Block Bearing Walls
The sequence includes:
- Mark layouts on foundations as per architectural drawings
- Prepare lime/cement mortar in specified mix proportions with optimal water content for cohesion
- Spread mortar bed on foundation plinth to receive the first masonry course
- Position masonry units like bricks/blocks checking alignments frequently
- Apply mortar on vertical joints to enable bonding with adjacent masonry course
- Use string lines stretched between both wall ends to ensure straight and levelled bedding
- Repeat laying successive masonry courses using bonding patterns like English/Flemish bonds
- Install weep holes intermittently at 900 mm vertical spacing for drainage
- Cure the masonry for stipulated durations preventing rapid moisture loss
Materials range from solid clay bricks, calcium silicate bricks, fly ash bricks, concrete blocks to dressed stone blocks. Veneeringexteriors with stone/glazed bricks offers aesthetic facades.
Mortar mixes are application specific – 1:6 cement-sand for foundations progressing to 1:4 and 1:3 for superstructure brickwork as strength needs decline. White cement improves mortar workability. Admixtures enhance properties.
Reinforcing masonry walls involves embedding steel reinforcement bars in preformed cavities at vertical junctures and lintels which are then grouted using micro concrete/mortar mixes. Geogrids offer stiffening benefits through confinement and composite action.
Anchoring arrangements like dash fasteners, ties and shelf angles aid integration with RCC members. Non-shrink grouts compensate settlement cracks.
Timber Stud Partition Walls
Stepwise construction involves:
- Fix sole plates using mechanical fasteners on finished floor along layout lines
- Position vertical studs made of timber/light gauge steel at designated spacing along plates and temporarily brace in plumb position
- Construct double top wall plates sandwiching waterproof building paper to protect wood
- Anchor wall framing to floor and ceiling structure using angles/joists
- Install insulation materials followed by attaching panels like plywood, particle boards on both sides using nails/adhesives
- Fix cover strips over joints between consecutive boarding pieces for seamless finish
- Apply jointing compound and sand adequately before priming and painting as desired
Timber studs, noggins and plates usually employ renewable softwoods like Pine, Douglas Fir etc. Structural sheathing materials include plywood, Oriented Strand Boards (OSB), cement-fiber boards and insulating boards using polystyrene etc.
Screws and bolts suit connections instead of nails for reliable restraint. Proprietary fasteners ease quick site assembly without compromising durability.
Glass Partition Wall Systems
Constructing demountable glass office partitions involves:
- Determine layouts of straight/curved glass walls, door locations etc.
- Install bottom tracks using mechanical fasteners ensuring flooring protection
- Erect interim braced stud framing to temporarily support glazing
- Position prefabricated glass doors/panels with edges encased in protective gasket into wall framing
- Level and fasten wall studs incorporating height-adjustable brackets to achieve storey heights
- Integrate aluminum door frames also housing functional hardware like locks, handles etc. as specified
- Insert rubber glazing strips, caps and weather seals for air/water tightness
- Apply neutral-cure silicone sealant for impermeable concealed joints
Toughened monolithic/laminated glass 8-12 mm thick gives elegant transparency. Onyx, quartz or granite stone inserts provide textural accents. Frameless glass walls with minimal steel posts underline structural lightness.
Framed walls may use decorative wooden frames, stainless steel or powder coated aluminum surronds. Ceiling hung systems liberate floorspace.
Drywall Metal Stud Partitions
Demographics: India’s population was over 1.39 billion in early 2022, making it the second most populous country in the world after China. Some key facts:
- India’s population growth rate is around 1% per year. At this rate, the population is projected to reach 1.53 billion by 2030.
- India has a relatively young population with a median age of 28 years, compared to 38 years in China and the United States.
- India is rapidly urbanizing, with an urbanization rate of around 2.4%. Currently 35% of Indians live in cities, with projections of 50% by 2030.
- The literacy rate has risen from around 65% in 2001 to almost 80% in the 2021 census. However, there is still progress to be made here.
Economy: India has one of the fastest growing economies in the world, averaging around 7% GDP growth annually in recent years. Key aspects include:
- India has the world’s 5th largest economy by nominal GDP. The economy crossed the $3 trillion mark in 2019.
- Services are the largest sector of the Indian economy, accounting for over 55% of GVA. Industry contributes about 30% and agriculture 15%.
- Major industries include information technology, telecom, automotive, pharmaceuticals, petrochemicals and mining. Software services and business process outsourcing are major growth sectors.
- India has become a global manufacturing hub in several sectors such as automobiles, pharmaceuticals, engineering goods, and electronics.
- However, issues like income inequality, unemployment, farmer distress and gender gap persist as major challenges. Reforms and policy initiatives are focused on addressing these.
So , India has tremendous promise and economic potential driven by its large, young population and rapid development across sectors. With progressive reforms and investments in human capital, India seems poised to unlock its immense growth possibilities in the coming decades. The focus on creating jobs and uplifting marginalized sections will be key.