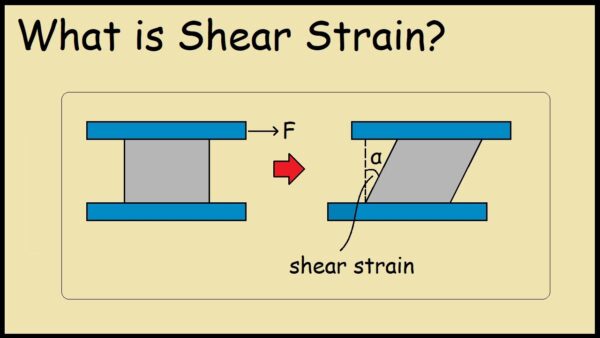
Tensile strength defines a material’s resistance to forces pulling it apart.
When designing load-bearing structures and components like bridges, pressure vessels, and dynamic machines, understanding the tensile strength of materials is imperative.
It defines the maximum stress or pulling force per unit area that a solid can withstand axially before fracturing.
It quantifies axial resistance and helps engineers assess if a system will endure expected tension and elongation effects from service conditions without mechanical instability or premature failure.
Compared to compressive strength against crushing, knowing the tensile limit is crucial for materials experiencing expansion or bending actions.
What is Tensile Strength?
It refers to the maximum stress a material can withstand when subjected to elongation or pulling forces before failing or breaking.
It measures the force per unit area (MPa or psi) required to pull a substance apart through expansion in length.

Tensile strength shows the material’s resistance to axial tension loading.
A strong tensile limit indicates it is rigid and can withstand high tension without deformation or cracking.
Defining Key Aspects
As an intensive material property, tensile strength depends on a substance’s composition and microstructure, not its size. Some key aspects in its definition:
- Maximum stress sustained in tension
- Point at which a brittle material fractures
- Point at which a ductile material incurs permanent plastic deformation
- Uniform elongation prior to necking down (in a tensile test)
Compare this against compressive strength (pushing force resistance).
Deriving the Formula
The basic strength formula is:
σts = F / A
Where:
σts = Tensile stress (Pa, psi)
F = Maximum load or force (N, lb)
A = Initial cross-sectional area (m2, in2)
So tensile strength quantifies maximum axial force per unit area at failure.
Key Differences: Tensile Strength vs Yield Strength
While related metrics, tensile and yield strength have some differences:
- Tensile strength indicates total breaking stress. Yield strength signals the onset of plastic deformation.
- Brittle materials have similar tensile and yield strengths. Ductile materials have yield strengths ~40% below their tensile strengths.
- Tensile strength is always higher than yield strength for ductile substances.
- Both depend on many factors like temperature, loading rate, processing method etc.
Ultimate Tensile Strength (UTS)
The tensile strength measured in a standard material test is called ultimate tensile strength (UTS).
UTS is determined using controlled universal tensile testing machines.
A sample undergoes gradual uniaxial tension until failure.
Engineers measure force applied and calculate UTS as stress at fracture point.
UTS data is important for performance evaluation and material selection for load-bearing structures.
Typical range for steels is 400-1550 MPa.
Step-by-Step Strength Testing Method
Testing mechanisms work by continually extending a test piece between two fixtures (the grips) until it ruptures:

The testing procedure involves:
- Securing test specimen between tensile grips
- Applying slow axial load force increasingly through grips
- Monitoring elongation vs tensile load with sensors
- Recording maximum tensile force (F) at instance of fracture
- Measuring original cross-sectional area (A)
- Calculating UTS by formula: UTS = F/A
The stress-strain curve plots the full material response.
Engineers analyze curves to design components that operate within safe boundaries below tensile limits.
Factors Influencing Tensile Strength
Many variables affect a material’s tensile stress, including:
- Processing method – Casting, rolling, extrusion, etc.
- Alloying elements – Carbon, manganese, nickel, chromium etc.
- Microstructure – Grain size, phase arrangement
- Heat treatment – Quenching, tempering, annealing
- Cold working – Prior plastic deformation
- Surface condition – Flaws, impurities
By optimizing these parameters, engineers can maximize tensile resistance.
Improving Strength of Steels
Various approaches enhance strength of steels:
- Alloying with nickel, manganese, or silicon
- Reducing grain size through thermal refining
- Precipitation or dispersion hardening treatments
- Introducing cold working prior to heat treatment
- Enhanced control over melting, casting and hot working
Modern QT and TMCP steels now reach 1300+ MPa UTS by precision microstructure tuning.
Examples of High Strength Materials
Materials boasting exceptional tensile strength include:
- Ultra-high-strength steels – 1300+ MPa strength for lightweight auto parts and aerospace.
- Graphene – 130 GPa strength; over 200 times stronger than steel. Ideal for nanocomposites.
- Carbon fiber – Up to 7 GPa radial strength. Used in balloons, sports gear and turbines.
- Tungsten – Extremely hard metal with UTS of 1510 MPa. Makes durable wires and alloys.
Ongoing development focuses on balancing strength with other properties like ductility for diverse applications.