Bulk molding compound (BMC) is a versatile thermoset plastic material used extensively in civil infrastructure projects.
This composite combines resins, reinforcement fibers, fillers, and other additives into a moldable compound.
When cured with heat and pressure, BMC forms rigid structural parts suitable for heavy load-bearing applications.
This article explores the major types, properties, processing methods, and uses of bulk molding compounds in civil construction.
Types of Bulk Molding Compounds
BMC formulations can be customized to meet specific material performance requirements. Common variants include:
- General purpose BMC – Balanced electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties at a low cost. Used for electrical housing, machine bases, and basic infrastructure parts.
- Low shrink/low profile BMC – Contains fillers to minimize visual defects from shrinkage. Provides superior dimensional stability crucial for precision civil engineering molds.
- Flowable BMC – Lower viscosity for highly detailed molds with thin walls or complex geometry. Allows excellent fiber wet-out and surface finish.
- Fire retardant BMC – Formulated with fire suppressing fillers to meet strict flammability standards in infrastructure projects. Enables use in electrical enclosures, smoke barriers, etc.
- Corrosion resistant BMC – Improved water, moisture, and chemical resistance with the addition of reinforcements like glass fibers. Used in pipe fittings, chemical storage tanks, drainage systems.
Bulk Molding Compound Manufacturers
Leading manufacturers offering customized BMC materials for civil engineering include Continental Structural Plastics, IDI Composites, LyondellBasell, Menzolit, Huayuan Advanced Materials, and Core Molding Technologies.
These companies maintain stringent quality control while formulating compounds to match application requirements in infrastructure construction.
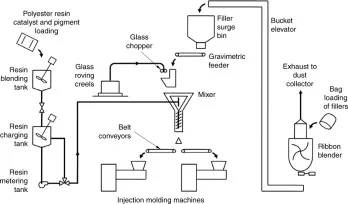
Bulk Molding Compound Properties
BMC combines a polyester, epoxy, or phenolic thermoset resin with reinforcing filler agents to produce a molding compound with these typical properties:
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Resistance to corrosive substances
- Dimensional stability in load bearing structures
- Excellent thermal and electrical insulating capacity
- Capability to mold complex and irregular shapes
- Good surface finish straight from the mold
- Cost savings versus traditional materials like steel or concrete
The filler ingredients (typically glass fibers, minerals, etc.) enhance the base resin’s structural integrity while lowering overall material expenses.
BMC’s balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and affordability make it suitable for underground water management systems, chemical storage tanks, trench covers, supportive bridge embankments, and other resilient civil infrastructure components.
Bulk Molding Compound Processing
BMC processing involves these key steps:
- Compounding – Thoroughly mix resin, reinforcements, fillers, and other additives into a putty-like molding compound. Deaerate to remove air pockets.
- Molding – Load BMC into heated molds, apply pressure to tightly pack material and initiate curing process.
- Curing – High temperature molding triggers chemical crosslinking as compound transitions from liquid to solid final state.
- Post-mold finishing – Trim and clean final BMC part to prepare for integration into infrastructure project.
Precision monitoring of process parameters like heating rate, pressure, mold temperature enables high quality, consistent production of BMC structural components.
Automated systems streamline large-scale molding suitable for major civil engineering installations.
Bulk Molding Compound Applications
Favorable affordability alongside weather, corrosion, and flame resistance drives widespread infrastructure applications such as:
- Underground utility boxes – House valves, wiring, and control equipment safe from soil/moisture contact.
- Trench covers – Durable steel/BMC composites prevent roadway cave-ins into subterranean infrastructure.
- Storm drains – Channels away rainfall runoff, resists chemical breakdown from groundpollutants.
- Manhole rings/covers – Strong yet lightweight for easy access below roads/pavements.
- Electrical junctions – Safely insulates power connections from environmental exposure.
- Structural support ribs – Strengthen bridge embankments.
- Pipe fittings – Withstand pressurized water flow while buried underground.
Bulk Molding Compound vs Sheet Molding Compound
While similar in composition, BMC and sheet molding compound (SMC) differ significantly in their production methods and infrastructure applications:
- Production: SMC starts as putty-like sheets preformed into rough part shapes. BMC is mixed as a viscous liquid then fully molded.
- Fiber orientation: SMC generally aligns fibers along sheet surface. BMC has more randomized 3D fiber orientations.
- Part size: SMC suits large, flat components like exterior panels or encasements. BMC better handles small, complex parts.
- Surface quality: SMC finish defined by sheet mold surface. BMC finish depends wholly on mold tooling.
- Uses: SMC for flat, visible exterior structures. BMC for mechanical housings, fittings, underground infrastructure.
Advantages of Bulk Molding Compounds
Key merits make BMC a regular choice for civil engineering projects:
Customizability – Tailor formulations to application demands. Vary resin chemistry and fillers/reinforcements.
Process efficiency – Short molding cycles. Fully automated production. Minimal secondary machining.
Strength properties – Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. Withstand heavy static or dynamic loads.
Corrosion performance – Resist damage from water, chemicals, road salts, weathering. Long service life.
Part integration – Inserts and attachments easily molded in. Enable fastening, hinging, fittings.
Flame retardance – Meet safety codes for infrastructure electrical components and barriers.
Bulk Molding Compound Suppliers
In addition to the major manufacturers producing BMC, many compounders offer custom formulation or on-demand inventory services.
They accept small-batch orders while handling raw material procurement and regulatory compliance.
This establishes consistent access to infrastructure-grade BMC. Leading composites suppliers include Avient, RTP Company, Premix, and Atlas Composite Materials.
Bulk Molding Compound Material Specifications
BMC falls under thermoset molding specification categories encompassing:
- Polyester BMC – Most economical option. General purpose strength and corrosion resistance.
- Epoxy BMC – Enhanced durability and dimensional stability. Preferred electrical insulation.
- Phenolic BMC – Maximum heat/flame resistance suitable for fire blocking structures.
International standard ASTM D6717 establishes testing procedures to quantify BMC mechanical, physical, electrical, and thermal properties during qualification.
Common metrics include tensile modulus, flexural modulus, Izod impact resistance, dielectric breakdown voltage, and peak exothermic temperature.
Bulk Molding Compound Custom Formulations
While standard BMC formulations suit most civil infrastructure needs, specialty custom blends target unique performance requirements, including:
- Ultraviolet resistance – For exterior structures facing long-term sun/weather exposure.
- Critical stress tolerance – Maximizing load capacity for heavyweight loading scenarios.
- Temperature extremes – From subzero cold to extreme heat fluxes.
- Chemical immunity – For highly corrosive soil conditions or fluid conduits.
- Microporosity – Minimizing permeation for underground fluid system sealing.
- Bonding capacity – Interlaminar adhesives tailored to substrate materials (metals, concrete, etc.)
Carefully engineered custom BMC unlocks infrastructure performance potential beyond standard offerings.






