What is Scaffolding?
Scaffolding provides temporary elevated platforms to safely support workers and materials during construction, repairs, and maintenance of structures and equipment. Scaffolds allow access to work areas above ground.
Purpose of Scaffolding
Here are some of the main purposes and functions of scaffolding in construction and civil engineering projects:
- Provide safe working platforms and access at height for workers to perform tasks like bricklaying, plastering, painting etc.
- Create adjustable and modular elevated stages to easily reach different working heights.
- Safely support workers, materials, tools and equipment like during facade work, formwork, steel fixing etc.
- Allow easy movement and material handling by providing large open platforms with access ramps or stairs.
- Protect workers from falls and injuries by providing a stable enclosed platform with guardrails, toe boards etc.
- Distribute heavy loads properly to base structure through erect scaffolding components like standards, ledgers etc.
- Provide access around structures and buildings during construction and maintenance activities.
- Temporarily support and brace formwork, existing structures and completed works during construction.
- Provide containment around buildings and sites by encapsulating with perimeter scaffolding.
- Allow step-by-step dismantling in inverse order of erection during demolition projects.
- The configurability and load bearing function of scaffolds make them an indispensable tool for safe and efficient construction.

Types of Scaffolding Systems
Here are the main types of scaffolding used in construction and civil engineering projects:
Supported Scaffolds
- Pole Scaffolds: Poles support platforms resting in cup brackets.
- Tube and Coupler: Prefabricated tubes connect with clamps.
- Fabricated Frame: Built with pipes, tube and fittings.
Suspended Scaffolds
- Swing Stages: Platforms suspended by ropes or cables.
- Boatswain’s Chairs: Single person seat suspended from roof.
- Boatswain’s chair – Single-person seated platform.
- Crawler system – Powered platform moves along building.
Perimeter Scaffolds
- Birdcage scaffolds – Contain work area on all sides.
- Independent runners – Shield building edges.
Rolling Scaffolds
- Tower Scaffolds: Frame scaffold on casters with guardrails.
- Rolling Gantries: Movable steel frame spanning over work area.
Specialty Scaffolds
- Shoring Scaffolds: Support vertical loads like formwork.
- Slope Scaffolds: Custom scaffolds for inclined slopes.
- Stair Scaffolds: Scaffold integrated with stair access.
- Side bracket scaffolds – Support formwork.
- Raking shores – Brace formwork diagonally.
- Dead shores – Temporary post-construction supports.
Temporary Scaffolds
- Single Scaffolds: Basic individual scaffold units.
- Double Scaffolds: Two platforms back-to-back.
- Mobile scaffolds – Rolling tower structures.
Proper selection of scaffolding type is based on the height, load, access requirements and complexity of the construction work. Each type has specific purposes and advantages.
Scaffolding Equipment Types
some of the main types of equipment used in scaffolding systems:
- Frames – Prefabricated welded frames or fabricated frames provide the structural shape and platform levels.
- Planks – Timber planks, metal decking or manufactured platforms create the horizontal work surface.
- Tubes – Steel or aluminum tubes used for standards, ledgers, diagonals, braces, guardrails etc. Main structural members.
- Couplers – Clamps like right-angle couplers, swivel couplers, putlog couplers etc. connect the tubes.
- Ties – Wire rope ties, bolt ties, wrap around ties secure scaffolds to buildings.
- Base Plates – Base jacks, sole plates, mudsills made of steel distribute loads onto ground.
- Boards – Special lightweight boards for loading platforms.
- Access Ladders – Hook ladders, stair stringers provide access to platforms.
- Wheels – Rigid or swivel casters allow mobility of rolling scaffolds.
- Props – Telescopic props support platforms and adjust heights.
- Fall Arrest Systems – Safety harnesses, lifelines secure workers from falls.
Selecting appropriate certified scaffolding equipment is essential to building safe and compliant scaffolds.
Different Scaffolding Components
Here are some of the main components that make up scaffolding systems:
- Standards – Vertical tubes that transfer scaffolding loads to the base. Main supports.
- Ledgers – Horizontal tubes that support the scaffolding platforms. Attach standards together.
- Transoms – Horizontal tubes placed perpendicular to ledgers for increased stability.
- Diagonals – Tubes connecting ledgers and standards diagonally to resist swaying.
- Braces – Tubes fixed diagonally between standards on sides of scaffold. Prevent racking.
- Base Plates – Flattened metal plates placed under scaffold standards to distribute loads.
- Planks – Horizontal platform boards made of wood or metal on which workers walk.
- Couplers – Clamps, fittings and fasteners that connect scaffold tubes.
- Ties – Wires or clamps securing scaffold to building or structure for stability.
- Access Ladders/Stairs – Provide access from ground to scaffold platforms.
- Guardrails – Railings and toe boards provide fall protection for workers on platform.
- Wheels/Casters – Allow rolling movement of mobile scaffolds.
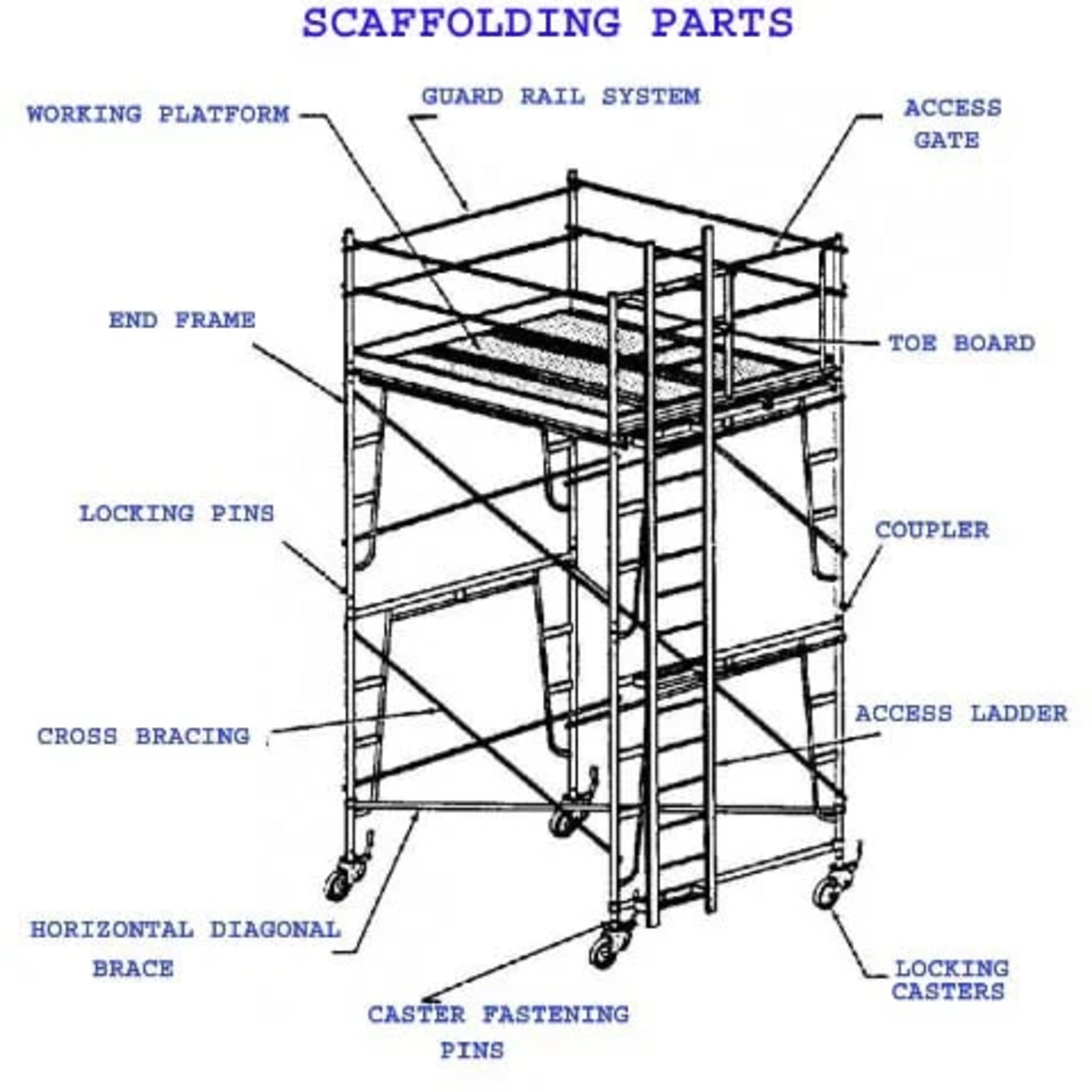
Proper assembly of these components ensures the scaffolding is structurally sound and safe.
Scaffolding Classifications
By Design Type
- Tube and Coupler – Prefabricated components connected with clamps. Most common modern type.
- Fabricated Frame – Built from tubes connected with fittings and joints. Customizable sizing.
- Pole Scaffolds – Platforms supported on poles inserted into metal sleeves. Quick assembly.
By material
- Metal Scaffolds – Steel or aluminum tubes and components. Strong but heavy.
- Wood Scaffolds – Timber structural standards, ledgers and planks. Lightweight.
By Structure and Stability
- Supported Scaffolds – Rely on building or structure for stability. Most common.
- Suspended Scaffolds – Hung by wires and ropes from roofs or ceilings.
- Self-Supporting Scaffolds – Freestanding with adequate bracing for stability.
By Usage
- Access Scaffolds – For worker access like platforms, stairs, ladders.
- Supporting Scaffolds – Carry loads like shoring, formwork, facade.
- Protection Scaffolds – Containment like debris nets, sidewalk sheds.
- Temporary Scaffolds – Short term works.
Proper classification helps determine the right scaffold type and application in construction projects.
Conclusion
Understanding the extensive range of scaffolding systems, components, materials and types allows proper selection and construction of safe and optimized scaffolds for any civil construction or maintenance need. Following scaffolding best practices and regulations prevents worker injury and project delays.




