Surveying is a crucial aspect of civil engineering, providing essential data for planning, designing, and executing projects. From topographic surveys to deformation monitoring, various types of surveys are employed to gather accurate and reliable information. In this blog post, we will explore the different types of surveys used in civil engineering and their applications.

List of Different Types of Surveys
1. surveying based on type of instruments
Here are some common types of surveys in civil engineering categorized based on the instruments used:
1.Total Station Surveys
- Trigonometric leveling surveys
- Traverse surveys
- Topographic surveys
2. GPS Surveys
- Control surveys
- Area surveys
- Alignment surveys
3. 3D Laser Scanning Surveys
- As-built surveys
- Deformation surveys
- Point cloud surveys
4. Photogrammetric Surveys
- Aerial surveys
- Mapping surveys
- Volumetric surveys
5. Leveling Surveys
- Differential leveling
- Profile leveling
- Cross sectional leveling
6. Theodolite Surveys
- Horizontal angle measurement
- Vertical angle measurement
- Tacheometric surveys
The choice of survey instrument depends on the requirement, accuracy needed and site conditions. Civil engineers use various instruments and survey types for design, planning and construction.
2. Surveying based on nature of survey
Topographic Survey:
This survey focuses on measuring and mapping the Earth’s surface, including natural and artificial features, elevations, and contours.
Techniques Used in Topographic Surveying
Topographic surveying involves measuring and mapping the Earth’s surface, including natural and artificial features, elevations, and contours. Techniques used in topographic surveying include:
- Terrestrial surveying using total stations and GNSS receivers
- Aerial surveying using drones or aircraft
- Photogrammetry and remote sensing
- Laser scanning and LiDAR technology
Cadastral Survey:
Also known as a boundary survey, this type of survey establishes or retraces property boundaries, easements, and other land divisions.
Boundary Surveying for Land Disputes
Boundary surveying, also known as cadastral surveying, establishes or retraces property boundaries, easements, and other land divisions. This type of surveying is crucial for resolving land disputes and ensuring accurate property documentation. Boundary surveyors use techniques such as:
- Researching historical records and deeds
- Locating and measuring boundary markers
- Using GNSS and total stations for precise measurements
- Preparing boundary maps and legal descriptions
Construction Survey:
These surveys are conducted before, during, and after construction projects to ensure proper alignment, grading, and positioning of structures.
Role of Surveying in Construction Projects
Surveying plays a vital role in construction projects, from the initial planning stages to the final completion. Surveyors provide essential data for:
- Site layout and staking
- Grading and excavation control
- Alignment and elevation control for structures
- As-built surveys for project documentation
Hydrographic Survey:
This survey maps underwater features, such as the depth, contours, and characteristics of water bodies like oceans, lakes, and rivers.
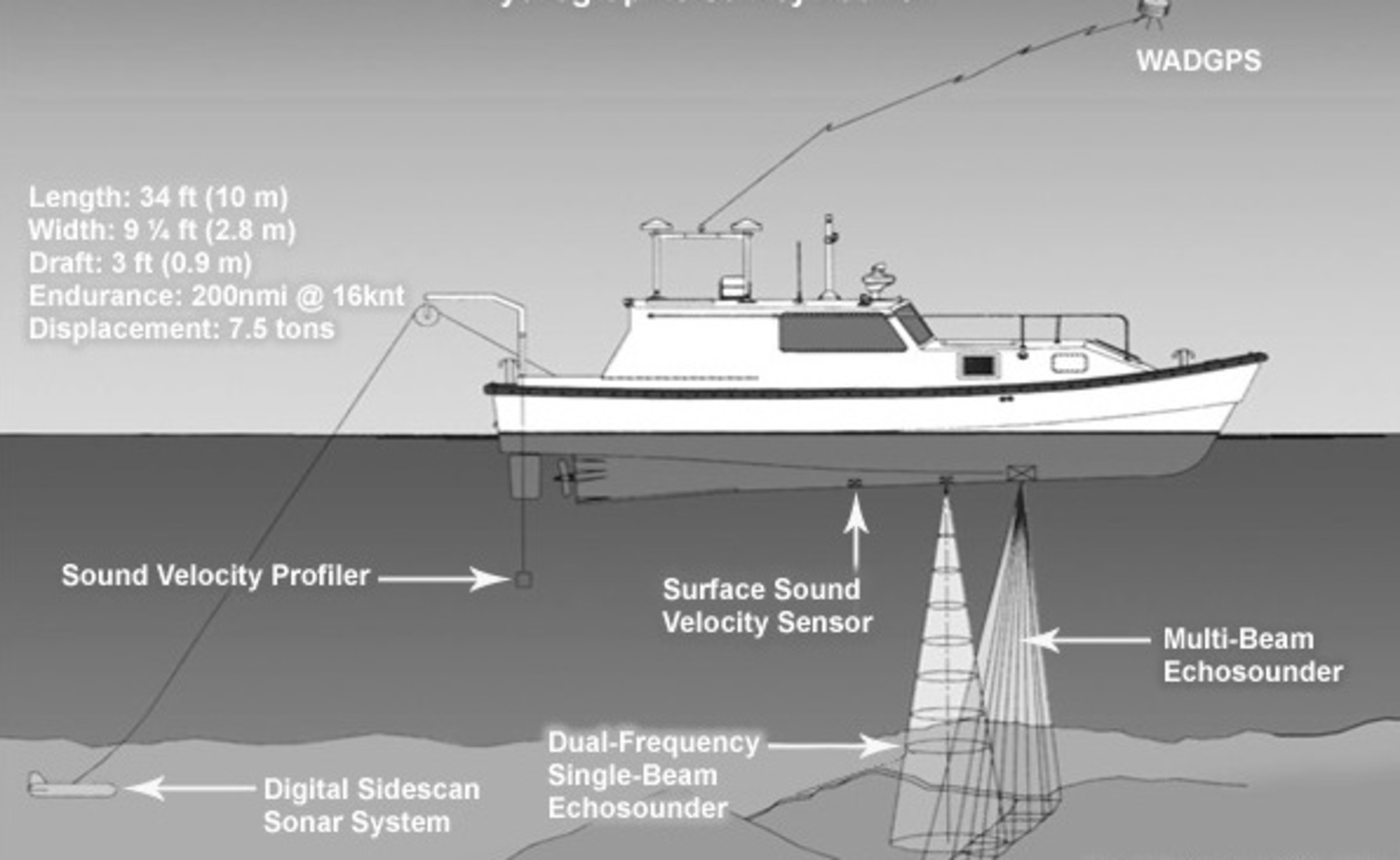
Hydrographic Surveying Equipment and Software
Hydrographic surveying maps underwater features, such as the depth, contours, and characteristics of water bodies. Specialized equipment and software used in hydrographic surveying include:
- Single-beam and multi-beam echo sounders
- Side-scan sonar and sub-bottom profilers
- Tide gauges and water level sensors
- Hydrographic surveying software for data processing and visualization
Geodetic Survey:
Geodetic surveys are large-scale surveys that take into account the Earth’s curvature and are used for establishing control points and datums.
Importance of Geodetic Surveying in Large-Scale Projects
Geodetic surveying is crucial for large-scale projects that require accurate positioning and mapping across vast areas. The importance of geodetic surveying lies in:
- Establishing precise control networks and datums
- Providing a consistent reference framework for other surveys
- Supporting infrastructure development and resource management
- Enabling scientific research and geophysical studies
Aerial Survey:
Conducted using aircraft or drones, aerial surveys capture images and data of the Earth’s surface from above, which can be used for mapping, monitoring, and analysis.
Applications of Aerial Surveying in Mapping
Aerial surveying captures images and data of the Earth’s surface from above using aircraft or drones. Applications of aerial surveying in mapping include:
- Topographic mapping and contour generation
- Land use and land cover mapping
- Environmental monitoring and change detection
- Infrastructure planning and management
GNSS Survey:
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) surveys use satellite technology, such as GPS, to determine precise positions and coordinates on the Earth’s surface.
Advantages of Using GNSS in Surveying
Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) technology, such as GPS, offers numerous advantages in surveying, including:
- High accuracy and precision in positioning
- Rapid data collection and processing
- Reduced dependence on line-of-sight measurements
- Compatibility with other surveying techniques and software
Archaeological Survey:
These surveys are used to locate, document, and study archaeological sites and artifacts, often employing non-invasive methods like remote sensing.
Archaeological Surveying Methods and Tools
Archaeological surveying is used to locate, document, and study archaeological sites and artifacts. Methods and tools employed in archaeological surveying include:
- Ground-penetrating radar (GPR)
- Magnetometry and resistivity surveys
- Laser scanning and photogrammetry
- GIS and remote sensing for site analysis and mapping
Mining Survey:
Mining surveys are conducted to explore, map, and monitor mineral resources, as well as to ensure the safety and efficiency of mining operations.
Mining Surveying for Safety and Efficiency
Mining surveying is essential for ensuring the safety and efficiency of mining operations. Mining surveyors use specialized techniques and equipment to:
- Map and monitor underground mine workings
- Design and layout mining infrastructure
- Monitor ground movement and subsidence
- Ensure compliance with safety regulations
Deformation Survey:
This type of survey monitors the movement and deformation of structures, such as buildings, bridges, and dams, over time to ensure their stability and safety.
Deformation Surveying Techniques for Structures
Deformation surveying monitors the movement and deformation of structures, such as buildings, bridges, and dams, over time. Techniques used in deformation surveying include:
- High-precision leveling and alignment surveys
- GNSS and robotic total stations for continuous monitoring
- Geotechnical sensors and instrumentation
- Data analysis and visualization software
conclusion
The various types of surveys used in civil engineering demonstrate the diversity and complexity of the surveying profession. From topographic surveys for mapping to deformation surveys for structural monitoring, each type of survey plays a critical role in providing accurate and reliable data for engineering projects.
By understanding the techniques, equipment, and applications associated with different types of surveys, civil engineers can effectively leverage surveying data to design, execute, and maintain successful projects.