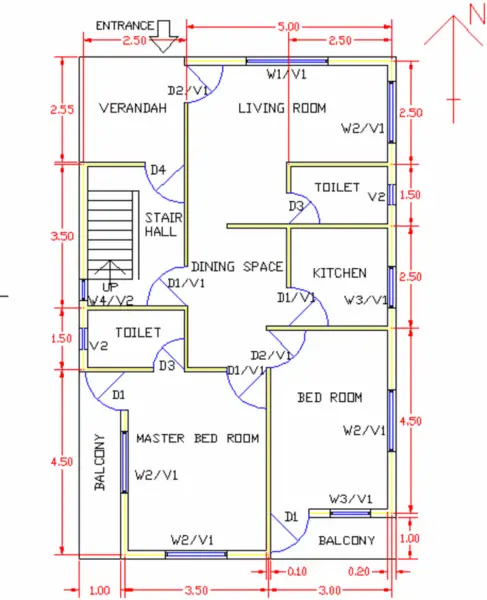
Stones have been used extensively in construction for thousands of years. As a civil engineer, having in-depth knowledge about the various types of stones, their characteristics and properties is very important.
understanding the various types of stones in civil engineering and their specific uses is crucial for ensuring the stability, durability, and aesthetics of the structures. Stones have been used as a building material for centuries, and their purpose extends beyond just providing a strong foundation.
The uses of stones in construction are diverse, ranging from creating sturdy walls and foundations to enhancing the visual appeal of buildings through decorative elements.
To determine the suitability of a stone for a particular application, civil engineers must consider the characteristics of good building stone. These include factors such as strength, hardness, durability, porosity, and resistance to weathering.
This comprehensive guide covers all the essential information you need to know about different stone types and their usage in construction.
Introduction
Stones can be classified into three major groups based on their mode of formation:
- Igneous Rocks: Formed from magma or lava when it cools down and solidifies. e.g. granite, basalt etc.
- Sedimentary Rocks: Formed by deposition of sediments and organic matter. e.g. limestone, sandstone etc.
- Metamorphic Rocks: Formed when existing rocks are changed by heat, pressure or chemical processes. e.g. marble, slate etc.
The type of stone selected for construction depends on factors like appearance, durability, strength, cost and availability. Engineers need to evaluate these factors carefully while deciding on the appropriate stone type for a project.
Stones Classification
Stones can be classified into three broad categories:
1. Natural Stone
This includes igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary stones that are available in nature. Examples: Granite, Basalt, Sandstone, Marble, Slate etc.
2. Artificial Stone
Stones manufactured by man using cement, aggregates and water. Examples: Concrete, Terrazzo etc.
3. Reconstituted Stone
Crushed stone which is recombined with adhesive material to reform the original stone. Example: Reconstituted marble.
Characteristics of Good Building Stones
- Strength: Should be able to withstand applied loads and forces.
- Durability: Ability to sustain harsh environmental conditions.
- Hardness: Resistance to surface abrasion.
- Toughness: Capacity to withstand impacts.
- Appearance: Should be visually appealing.
- Workability: Easy to cut, dress and create desired shapes.
- Cost: Should be available at reasonable and affordable price.
- Density: Heavier stones are stronger.
- Porosity: Stone should have low absorption.
- Weathering: Should resist effects of weathering.
Now let’s discuss the commonly used natural stone types in detail:

Types of Stones Used in Construction
Types of stones in civil engineering include marble, sandstone, slate, and basalt, each with its unique properties and uses of stones in construction.
Marble, with its elegant appearance, is often used for flooring, countertops, and decorative elements.
Sandstone, due to its relatively soft nature, is easy to shape and is used for building facades and ornamental work. Slate, known for its durability and water resistance, is an excellent choice for roofing and flooring applications.
following are some important stones and their characteristic properties that are used in construction.
Granite
Granite is an igneous rock formed by slow cooling and solidification of magma. It has a crystalline texture and is composed mainly of quartz and feldspar.
Characteristics:
- Extremely hard and durable.
- Resists weathering and abrasion.
- Can take polish and lustrous finish.
- Wide variety of colors and textures.
- Can sustain large pressure loads.
- Dimensional stability.
- Uses: Building cladding, monuments, countertops, flooring etc.
Basalt
Basalt is also an igneous rock formed by solidification of lava near the earth’s surface. It has fine grained mineral texture.
Properties:
- Very high durability and hardness.
- Good resistance to weathering and chemicals.
- Density provides excellent strength.
- Available in black color with dull luster.
- Can be polished for fine appearance.
- Applications: Aggregates, road construction, floor tiles, building veneers.
Marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock produced from limestone when subjected to heat and pressure. It has a crystalline texture and comes in wide variety of colors and patterns.
Characteristics:
- Medium hardness and durability.
- Takes smooth polish and has aesthetic appearance.
- Allows intricate carving and shaping.
- Vulnerable to staining and etching from acids.
- Uses: Sculptures, monuments, countertops, floor and wall tiles.

Slate
Slate is also a metamorphic rock formed by alteration of shale under heat and pressure. It has a fine grained foliated structure that allows it to split into thin sheets.
Properties:
- Highly durable, fire resistant and waterproof.
- Distinctive color ranges from purple, green to black.
- Easy to split into thin slabs and cut into shapes.
- Immune to weather effects with low water absorption.
- Applications: Roofing, flooring, chalkboards, table tops, cladding.
Sandstone
Sandstone is a sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand sized quartz particles cemented together. It is porous, hardy and easy to work with.
Characteristics:
- Available in a variety of colors like red, brown, yellow, grey.
- Simple quarrying and dressing process.
- Resistant to weathering effects.
- Moderate strength and hardness.
- Uses: Ornamental stone, paving, roofing tiles, aggregates.
Limestone
Limestone is a common sedimentary rock consisting of calcium carbonate minerals like calcite. It has a granular texture with various fossil formations.
Properties:
- Relatively soft and porous. -Soluble in acidic solutions and water.
- Easy to cut, dress and carve detailed shapes.
- White color varieties used extensively for ornamental work.
- Applications: Cement manufacturing, Aggregates, Sculptures, Cladding.

Gneiss
Gneiss is a metamorphic rock with alternating bands of light and dark colored minerals giving it a distinctive foliated texture.
Characteristics:
- Very hard and durable with high compressive strength.
- Varied colors ranging from dark gray to pink.
- Resists weathering and deleterious action of minerals.
- Difficult to cut and dress uniformly.
- Uses: Building cladding, crushed stone, monuments, flooring.
Conclusion
The type of stone selected in civil engineering construction greatly impacts the aesthetics, performance and durability of structures.
As an engineer, carefully evaluate the characteristics and properties of different stone types like strength, hardness, appearance, workability etc. before deciding on the appropriate material for your project.
Understanding the types of stones and their usage in civil engineering, professionals can make informed decisions when selecting materials for their projects, ensuring that the structures they build are not only functional but also visually appealing and long-lasting.
I hope this guide summarizes all the key information you need to know about the different types of stones used in construction.