Building a new structure, whether it’s a home, deck, or addition, requires a solid foundation. Two popular options are helical piers and concrete footings.
Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, making the choice dependent on various factors.
This article delves into the intricacies of both foundation systems, providing a comprehensive understanding to help you make an informed decision.
Keywords: Helical piers, concrete footings, foundation, construction, soil stability, installation, cost, advantages, disadvantages
Understanding the Basics
1. Concrete Footings: These are poured concrete bases that distribute the weight of the structure over a larger soil area. They are typically used in conjunction with concrete foundation walls or piers.

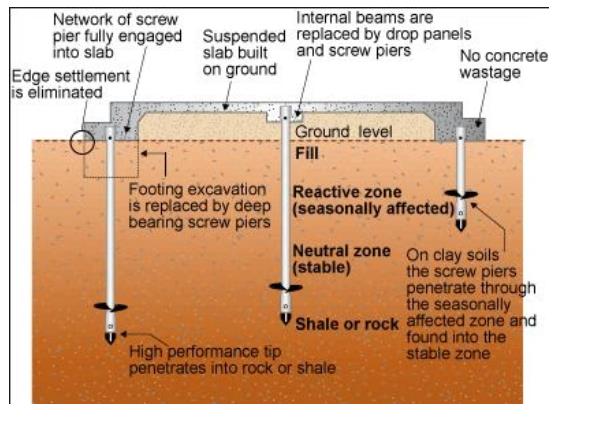
2. Helical Piers: These are steel shafts with helical plates welded to them, resembling giant screws. They are driven deep into the ground, bypassing unstable soil layers, until they reach competent, load-bearing soil.
Advantages and Disadvantages: A Comparative Analysis
| Feature | Helical Piers | Concrete Footings |
|---|---|---|
| Installation | Faster, less disruptive, all-weather installation | Time-consuming, requires excavation & curing time |
| Soil Types | Ideal for expansive, weak, or unstable soils | Limited use in such soils, prone to shifting |
| Load Capacity | Can handle heavy loads, adjustable for precise support | Load capacity depends on soil quality and depth |
| Cost | Generally more expensive upfront | Usually cheaper initially, but repairs can be costly |
| Durability | Highly resistant to corrosion, long lifespan | Susceptible to cracking and deterioration over time |
| Environmental Impact | Minimal soil disturbance, less waste generated | Excavation and concrete production impact environment |
| Accessibility | Installation possible in tight spaces | Requires ample space for equipment and materials |
| Repairs | Easier to repair or adjust if settling occurs | Repairs can be complex and expensive |
When to Choose Helical Piers
Helical piers are an excellent choice when:
- Soil conditions are poor: Expansive clay, high water tables, or loose soil can compromise concrete footings. Helical piers bypass these layers to reach stable ground.
- Speed is crucial: Projects with tight deadlines benefit from the quick installation of helical piers.
- Minimal disturbance is desired: Helical piers are ideal for existing structures, minimizing damage to landscaping or surrounding areas.
- Heavy loads are expected: Decks, additions, or structures requiring significant support benefit from the high load capacity of helical piers.

When to Choose Concrete Footings
Concrete footings are a suitable option when:
- Stable soil conditions exist: Firm, well-drained soil provides a solid base for concrete footings.
- Budget is a primary concern: Concrete footings typically have lower upfront costs compared to helical piers.
- Local building codes mandate them: Some areas have specific requirements for foundation types.
FAQs: Addressing Common Queries
1. How deep are helical piers installed?
The depth varies depending on the soil profile and load requirements. Engineers determine the appropriate depth through soil tests to ensure the piers reach competent load-bearing strata.
2. Are helical piers as strong as concrete footings?
Yes, helical piers can be equally strong or even stronger than concrete footings. Their load capacity is determined by the size and number of helical plates, allowing for precise adjustments based on the structure’s weight.
3. How long do helical piers last?
Helical piers are highly durable and can last for generations with minimal maintenance. The galvanized steel construction makes them resistant to corrosion.
4. Can helical piers be used for existing structures?
Yes, helical piers are an excellent solution for stabilizing and lifting existing foundations that have settled or shifted.
5. Do I need a permit for helical pier installation?
Building codes and permit requirements vary by location. It’s crucial to consult with local authorities and obtain necessary permits before starting any foundation work.
How-To: Installing Helical Piers
While it’s best to leave the installation to experienced professionals, understanding the process can be beneficial:
Step 1: Site Evaluation and Engineering: A qualified engineer assesses the soil conditions and determines the required pier size, depth, and placement.
Step 2: Marking Pier Locations: The engineer marks the precise locations for each pier based on the structural plans.
Step 3: Driving the Piers: Specialized hydraulic equipment drives the helical piers into the ground. Torque readings are monitored to ensure proper installation depth and load capacity.
Step 4: Brackets and Connections: Once the piers reach the desired depth, brackets are attached to connect them to the structure’s beams or foundation.
Step 5: Backfilling and Grading: The area around the installed piers is backfilled and graded to ensure proper drainage and aesthetics.
Conclusion
Choosing between helical piers and concrete footings is a crucial decision that impacts the structural integrity and longevity of your project. Carefully consider the factors discussed, consult with qualified professionals, and select the foundation solution that best suits your specific needs and site conditions.
