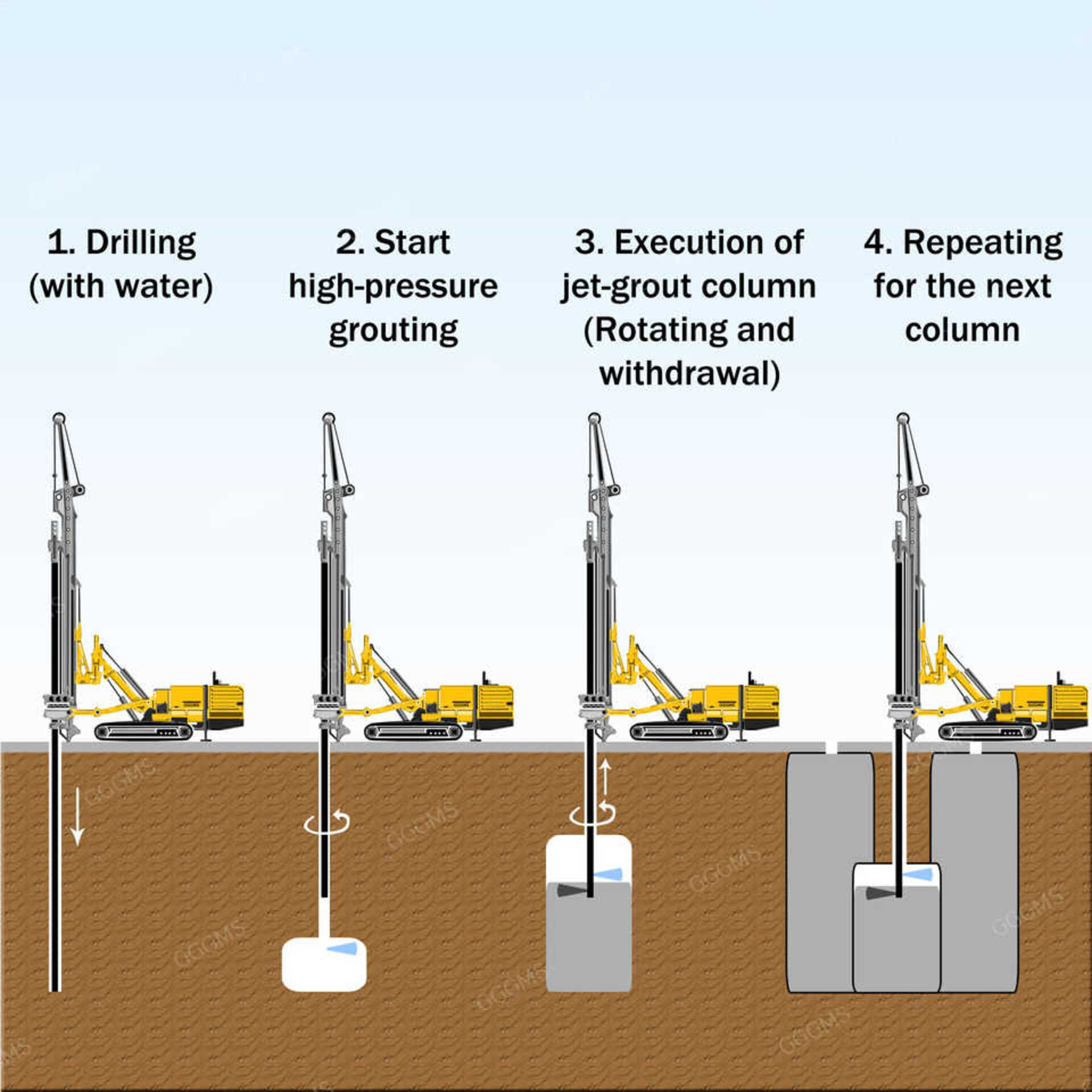
Jet grouting is a versatile ground improvement technique that has become increasingly popular in recent years. It involves the mechanical mixing of high velocity grout jets with native soil to form stiff cemented soil columns.
When designed and executed properly, jet grouting provides exceptional improvements in strength, permeability, and soft ground stability. However, realization of these benefits requires adherence to certain vital jet grouting design principles.
By understanding the fundamental jet grouting design concepts, engineers can produce robust and efficient ground improvement systems meeting project needs.
Knowledge of the principles allows for informed design decisions regarding applicability, constructability, economics, and performance.
design principles of jet grouting
Jet grouting is an innovative soil improvement technique that involves injecting grout at high speeds to mix with and strengthen the existing soil. When designing jet grouting program, engineers must consider several key principles to ensure success.
- The first principle is understanding the site conditions and soil properties.
Factors like soil type, strength, permeability, and depth influence the jet grouting design and feasibility.
For example, jet grouting may not work well in very coarse soils that the grout cannot adequately permeate.
Jet Grouting Design Equations
Here are 5 common formulas used in jet grouting design:
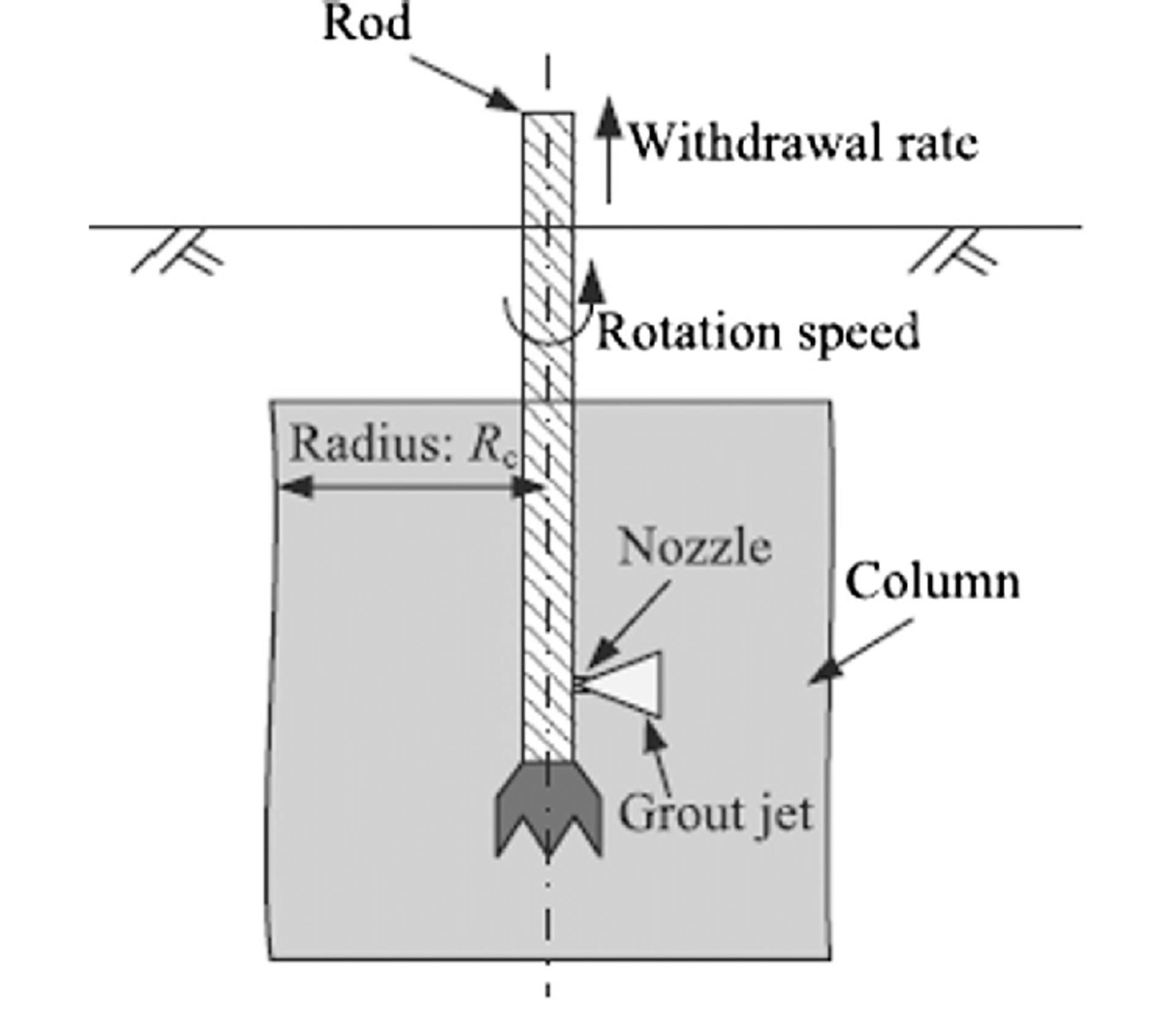
- Jet grouting column diameter:
D = d + k√P
Where:
D is the column diameter (in cm or inches)
k is constant based on soil characteristics (typically 2-4 cm/√bar)
P is injection pressure (bar or psi)
d is the nozzle diameter (cm or inches)
- Column spacing:
S = (1.5-2.0)D
Where:
S is the center to center spacing between columns
D is the column diameter
- Soil improvement area:
A = πD2/4S2
Where:
A is the treated soil area
D is the column diameter
S is the column spacing
- Cement grout consumption:
V = (πD2/4)Lρc
Where:
V is the grout volume per meter column length
D is the column diameter
L is the column length
ρc is the density of cement grout
- Minimum binding grouting pressure:
P = σcv
Where:
P is minimum grouting pressure
σcv is unconfined soil strength
2. The second vital principle is selecting the right jet grouting parameters like nozzle size, grout pressure, rotation speed, and withdrawal rate.
These impact grout penetration, mixing, and the properties of the treated columns. Computer modeling can help optimize the parameters.
3. Third principle is to check the spacing, size, and overlap of the jet grouted columns which is also critical.
The columns must interconnect to form a continuous mass with the targeted strength and permeability. Field testing verifies if the spacing and overlap are adequate.
4. Finally, the grout mix design influences the structural integrity and durability of the treated ground.
The mix must permeate the soil without bleeding or segregating. Trials are often needed to optimize the grout constituents and proportions.
Following these jet grouting principles allows geotechnical engineers to develop designs that successfully improve the ground.
Careful planning, testing, and monitoring ensures the system meets the project’s unique needs and soil conditions.
conclusion
Jet grouting is an extremely useful geotechnical tool when thoughtfully implemented.
However, lack of adherence to appropriate design principles can lead to ineffective or failed ground improvement efforts.
The critical jet grouting design concepts include comprehensive site characterization, proper parameter selection, column geometry and spacing, and optimized grout mixes.
Following structured design procedures that account for these technical fundamentals as well as economic and construction considerations will ultimately determine project success.
With the right design approach, jet grouting provides unmatched benefits for improving weak and problematic soils to deliver enhanced structural stability and performance.
Strict design principle conformance paired with quality assurance and control allows jet grouting to elevate infrastructure safety and resilience.







Hi, good morning.
Thanks for this information.
I would appreciate to learn more, if you could share me a sample of the jet grout design for a 14m deep excavation. I will attach the soil report once you consider the above. Thanks a lot. engr Jose MGenciana