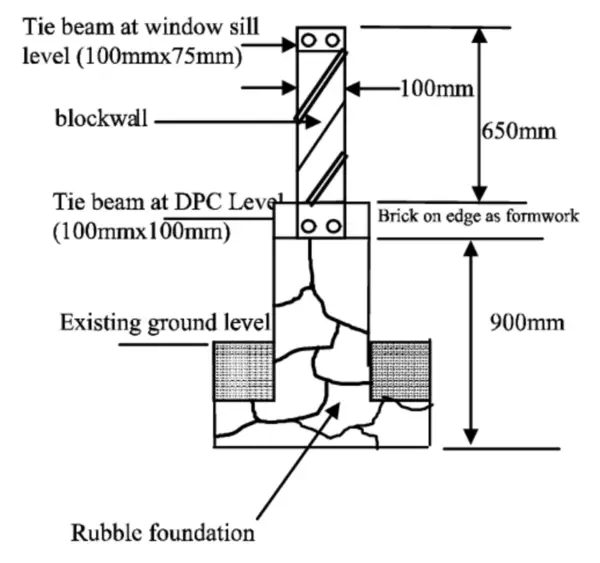
Tie beam details are a constant focus in the construction industry . These unsung heroes of the construction industry play a vital role in the overall structural integrity of a building, and understanding their specific design elements is crucial for ensuring the long-term stability and safety of any structure.
From the placement of reinforcement to the precise calculations of load-bearing capacity, the details of tie beam design are a delicate dance of engineering expertise and practical considerations.
At the heart of tie beam details lies the need for meticulous planning and execution. Shear and flexural reinforcement must be carefully positioned to counteract the various forces acting on the beam, while the connection to the supporting columns must be designed with the utmost precision to ensure a seamless transfer of loads.
In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the various aspects of tie beam details, exploring the nuances of reinforcement layout, shear and flexural calculations, connection design, and more. By understanding these critical details, civil engineers can create tie beams that are not only structurally sound but also cost-effective and efficient.
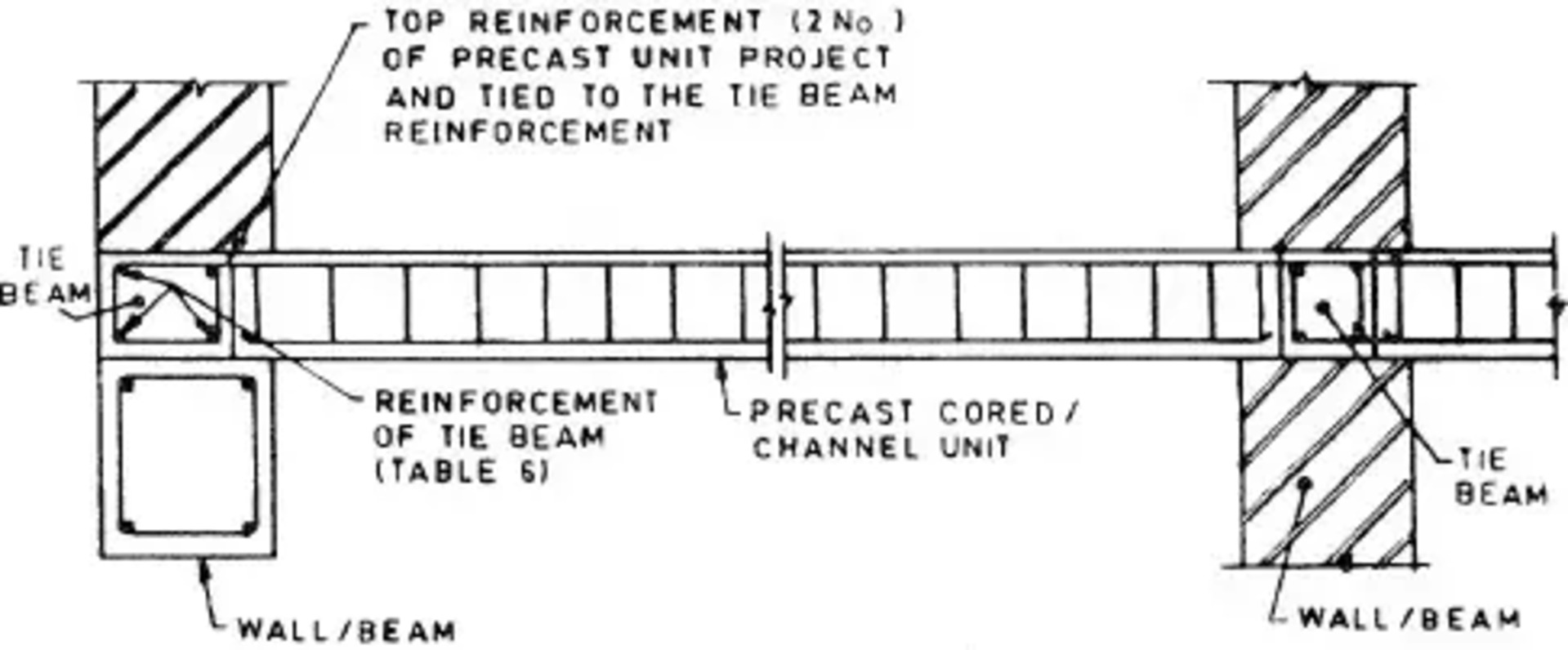
Tie beam details
Reinforcement Layout and Spacing
Tie beam reinforcement details plays a very important role in the structural integrity. The placement and spacing of the reinforcement within a tie beam are crucial for its structural performance. The longitudinal and transverse reinforcement must carefully designed to resist the various forces acting on the beam, including bending, shear, and torsion. The reinforcement layout must be optimized to ensure that the beam can withstand the expected loads without excessive cracking or deformation.
Shear Stirrup Design and Placement
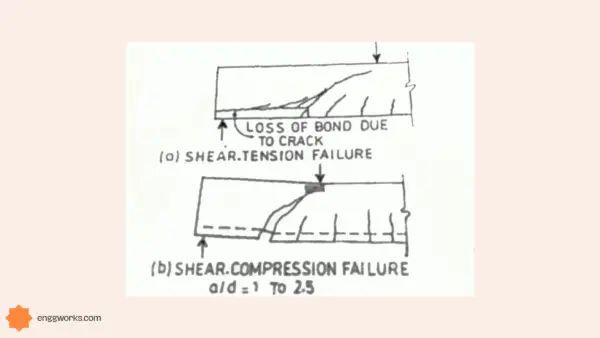
The design and placement of shear stirrups within a tie beam are essential for its resistance to vertical shear forces. Required stirrup spacing and size must be calculated based on the beam’s dimensions, the anticipated loads, and the concrete’s shear strength. Proper stirrup detailing can significantly enhance the beam’s overall structural integrity.
Flexural Reinforcement Calculations
Determining the appropriate flexural reinforcement for a tie beam is a critical step in the design process. Civil engineers must carefully calculate the required steel area and placement to ensure that the beam can resist the bending stresses induced by the various loads. This analysis often involves the use of established design equations and software tools to optimize the reinforcement configuration.
Tie Beam to Column Connection Details
The connection between the tie beam and the supporting column is a crucial aspect of the overall structural design. Civil engineers must ensure that the transfer of loads between these two critical elements is seamless and efficient. This may involve the use of specialized connection details, such as dowels, anchors, or even reinforced concrete corbels, to create a robust and stable interface.
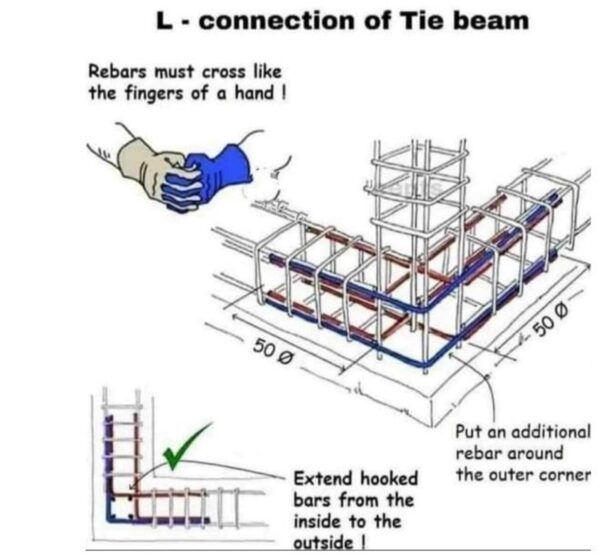
Residential Tie Beam Detailing Best Practices
In the residential construction sector, the detailing of tie beams is particularly important, as these elements are often the foundation for the entire structure. Best practices for residential tie beam detailing include ensuring proper concrete cover and clear spacing for the reinforcement, optimizing the lap splice lengths, and incorporating crack control measures to enhance the beam’s durability and long-term performance.
Commercial Tie Beam Detailing Requirements
Commercial structures often have more stringent requirements for tie beam detailing, as they are typically larger and subject to more significant loads. Factors such as the building’s occupancy, the type of construction, and the local building codes must be considered when designing the tie beam details. This may involve increased reinforcement, specialized connection details, and more complex rebar configurations to meet the specific needs of the commercial project.
Crack Control Reinforcement Design
Cracking in tie beams can compromise their structural integrity and durability, making crack control a critical design consideration. The reinforcement layout and concrete mix must be carefully designed to minimize the risk of cracking under various loading conditions. This may involve the use of specialized crack control reinforcement, such as additional stirrups or distributed reinforcement, to enhance the beam’s resistance to cracking.
Construction Sequence and Techniques
The construction of a tie beam is a meticulous process that requires careful planning and execution. Civil engineers must consider the construction sequence, ensuring that the formwork, reinforcement placement, and concrete pouring are carried out in a manner that promotes the beam’s structural integrity. Additionally, construction techniques, such as proper compaction and curing, can significantly impact the long-term performance of the tie beam.
Rebar Configuration and Lap Splices
The configuration and placement of the reinforcing steel within a tie beam are crucial design elements. The required rebar size, spacing, and lap splice length should be carefully calculated to ensure that the beam can withstand the expected loads. Proper tie beam rebar detailing can enhance the beam’s strength, ductility, and overall structural performance.
Concrete Cover and Clear Spacing Specifications
The concrete cover and clear spacing between the reinforcement in a tie beam are essential for its durability and long-term performance. Industry standards and local building codes are to be considered when specifying these design parameters, ensuring that the reinforcement is adequately protected from environmental factors and that the concrete can flow freely during the pouring process.
Conclusion
Mastering the intricacies of tie beam details is a cornerstone of civil engineering excellence. By understanding the nuances of reinforcement layout, shear and flexural design, connection detailing, and construction techniques, engineers can create tie beams that are not only structurally sound but also cost-effective and efficient.
As the foundation of our built environment, the humble tie beam deserves the utmost attention and care, serving as the unsung hero that supports the structures we rely on every day.