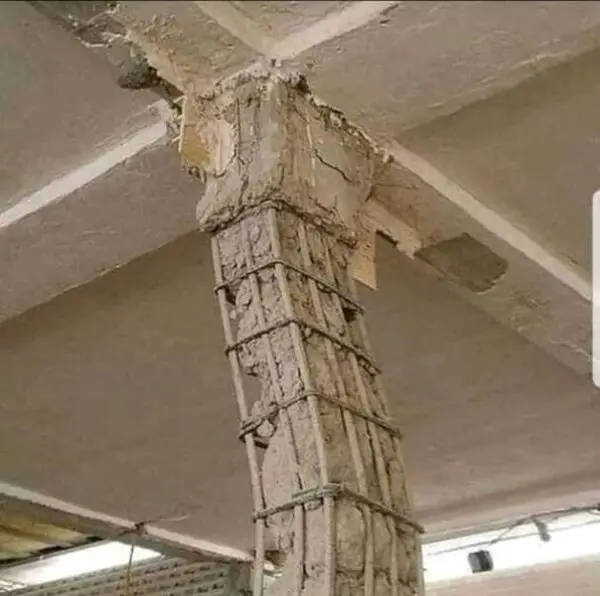
Before getting straight to the topic, let’s have a small discussion regarding aggregates. Did you ever wonder, why aggregates are typically used in construction and engineering projects?
Have you asked yourself why is it necessary to use aggregates and what is their importance?
What happens if at all aggregates are not available in a particular project or location or not in a surplus quantity? Is there any alternative for aggregates?
These questions generally revolve in the mind of a person who belongs in construction or contractors or in research or in a technical field of engineering.
In order to wrap up these queries one needs to have a good understanding regarding aggregates which we are about to talk about in our article.
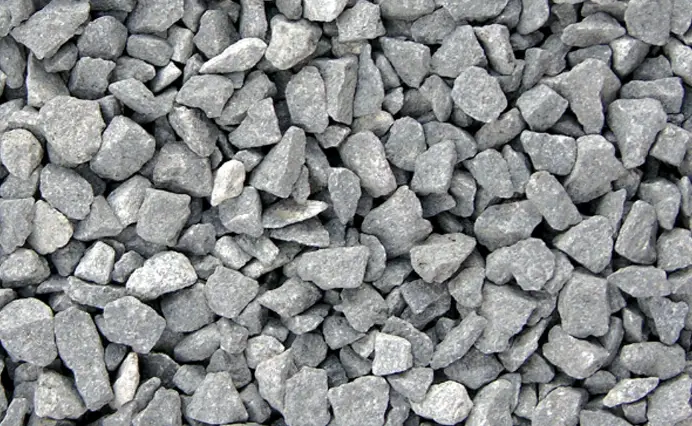

What are the aggregates used in concrete?
Various aggregates are used in concrete to provide strength, durability and volume to the mix. The main aggregates used in concrete are fine aggregates and coarse aggregates. The combination of both fine and coarse aggregates in cement paste or mortar produces concrete. Both coarse aggregates and fine aggregates are discussed in detail.
In particular, one has to know the importance of aggregate to know the tests and its quality. If you want to save money and build better bondage with cement, aggregate quality and standards are to be met.
Without knowing the type and aggregate influence in concrete, you will stumble upon lot of problems at later stages of the process. To avoid these, thorough knowledge of aggregate is necessary.
Coarse Aggregates
- Coarse aggregates are an essential part of concrete. The size of coarse aggregates usually ranges from 80 mm to 9.5 mm ( > 4.75 mm) in diameter.
- Common types of coarse aggregates include gravel, crushed stone, and recycled materials like blast furnace slag and demolition waste.
- These aggregates should be free from deleterious substances,alkali, organic matter, disintegrated pieces and should be hard, strong, dense, clean and durable.
- In addition to giving concrete strength, volume, stability, and improved resistance to abrasion and freezing and thawing cycles, coarse aggregates also increase the material’s strength.

Fine aggregates
- Fine aggregates are small- sized particles of sand, gravel, crushed stone , or other natural or artificial materials whose size usually ranges from 4.75 mm to 0.07 mm ( < 4.75 mm) in diameter.
- These aggregates are obtained naturally or manufactured; naturally from river beds, lakes or quarries or produced from industrial processes such as blast furnace slag or fly ash.
- Fine aggregates are used to fill the gaps between the coarse aggregates and the cement mortar to bind them together and improve the workability, strength of the concrete.
- The standard sand ( IS 650) in India is Ennore sand from Tamil Nadu and should be free from silt.