Cement is one of the most essential building materials in India, used for various construction purposes such as homes, offices, bridges, roads, etc.
The cement industry in India is one of the largest in the world, with a production capacity of over 500 million tonnes per annum.
However, the cement price in India is not uniform across the country, as it depends on various factors such as location, brand, quality, grade, and demand-supply dynamics.
In this blog post, we will provide an overview of the current cement price in India for different grades and brands of cement.
We will also discuss some of the factors that influence the cement price and the trends that are likely to shape the industry in the future.

Cement used in Construction
Depending on the particular needs of the project, both Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) and Portland Pozzolana Cement (PPC) are frequently employed in building.
OPC is frequently used in ordinary construction tasks including plastering, concrete, and mortar. There are three grades of it: 33, 43, and 53.
Whereas pozzolanic substances like fly ash, volcanic ash, or calcined clay are combined with Portland cement to create PPC.
It is employed in large-scale concrete projects, marine constructions, and sewage systems and has better workability and durability than OPC.
In conclusion, OPC and PPC both offer special qualities and applications in the building industry. The project’s unique requirements will determine which of the two types of cement is best.
Current Cement Price in India
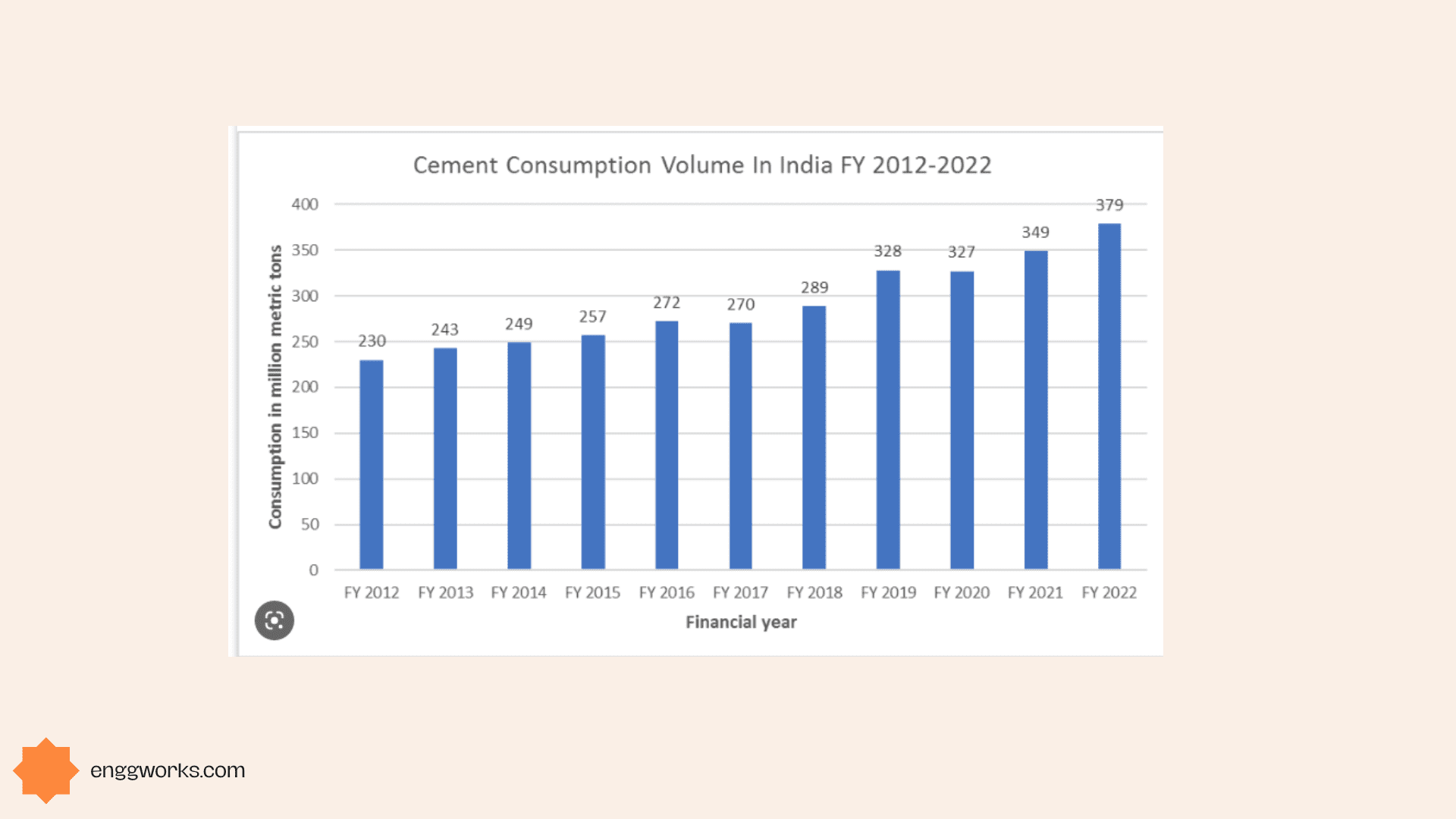
According to Statista, the average cement price in India reached 298 Indian rupees per 50 kg bag (or about Rs. 6 per kg) in 2021.
The price has seen a steady increase since 2018 when it was around Rs. 4 per kg. The cement price was projected to increase further to 307 rupees per bag (or about Rs. 6.14 per kg) by 2022.
However, these are only average prices and may vary significantly depending on the location and brand of cement.
The following tables show some examples of cement prices for different brands and grades of OPC and PPC for 50kgs bag is given below:
OPC 53 grade cement price list in India
| Cement Brand | Cement Grade | Price(Rs) per Bag |
| UltraTech Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 430 |
| Ambuja Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 420 |
| ACC Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 385 |
| Shree Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 330 |
| Ramco Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 430 |
| Dalmia Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 450 |
| JK Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 390 |
| Birla Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 440 |
| Jaypee Cement | 53 Grade OPC | 380 |
OPC 43 grade cement price list in India
| Cement Brand | Cement Grade | Price(Rs) per Bag |
| UltraTech Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 330 |
| Ambuja Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 330 |
| ACC Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 375 |
| Shree Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 350 |
| Ramco Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 315 |
| Dalmia Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 305 |
| JK Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 280 |
| Birla Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 300 |
| Jaypee Cement | 43 Grade OPC | 320 |
OPC 33 grade cement price list in India
| Cement Brand | Cement Grade | Price(Rs) per Bag |
| UltraTech Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 280 |
| Ambuja Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 290 |
| ACC Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 275 |
| Shree Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 265 |
| Ramco Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 250 |
| Dalmia Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 260 |
| JK Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 280 |
| Birla Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 250 |
| Jaypee Cement | 33 Grade OPC | 270 |
PPC price list in India
| Cement Brand | Cement Grade | Price(Rs) per Bag |
| UltraTech Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 365 |
| Ambuja Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 368 |
| ACC Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 400 |
| Shree Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 310 |
| Ramco Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 270 |
| Dalmia Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 325 |
| JK Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 375 |
| Birla Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 340 |
| Jaypee Cement | 53 Grade PPC | 370 |
Differences between OPC and PPC
PPC and OPC are two types of cement that are widely used in construction. PPC stands for Portland Pozzolana Cement, while OPC stands for Ordinary Portland Cement. Both have their own advantages and disadvantages, depending on the application and environment.
| Factors | OPC | PPC |
| Raw Materials | Made from clinker and gypsum | Made by blending OPC with pozzolanic materials like fly ash, volcanic ash, or calcined clay |
| Setting time | It has a faster setting time than PPC, which means that it hardens more quickly. This makes it suitable for use in situations where fast setting time is required. | The setting time of PPC is higher than OPC. Its slower setting helps to get better finishing. |
| Strength | It has higher initial strength than PPC. It is more compatible with admixtures and additives. It has better quality control and consistency. | PPC has better workability and strength than OPC. PPC produces more cohesive concrete, which results in better durability and resistance to corrosion. |
| Heat of hydration | Generates more heat during the hydration process than PPC and may cause thermal cracks in large concrete structures | It has a lower heat of hydration, making it suitable for use in large construction projects. |
| Cost | Costlier than PPC | Cheaper than OPC due to the lower cost of the pozzolanic materials used in its production. |
| Environmental impact | It is less eco-friendly as it emits more carbon dioxide during production | It is more eco-friendly as it uses industrial waste materials |
| Shrinkage | It consumes more water and has higher shrinkage | It consumes less water and has lower shrinkage |
| Application | OPC is widely used for general construction purposes due to its fast setting time | PPC has better workability and strength, making it more suitable for use in mass concrete works, marine structures, and sewage works |
Factors Influencing Cement Price in India
The cement price in India is influenced by several factors such as:
Demand-supply dynamics
The demand for cement is driven by various factors such as population growth,urbanization, infrastructure development,government policies,and seasonal variations.
The supply of cement is determined by factors such as production capacity,raw material availability,transportation costs,and market competition.
When demand exceeds supply or vice versa,the cement price tends to fluctuate accordingly.
Location
The location of a state or city can affect its cement price due to differences in transportation costs,taxes,and local market conditions.
For example, cement prices tend to be higher in remote or hilly areas where transportation costs are higher than in urban or plain areas where transportation costs are lower.
Brand
The brand name and reputation of a cement manufacturer can also influence its pricing strategy.
Some well-established brands such as Ultratech,Ambuja,and ACC may charge higher prices than other brands due to their perceived quality,trustworthiness,and customer loyalty.
However,some customers may prefer cheaper or local brands due to budget constraints or personal preferences.
Quality
The quality and grade of cement can also affect its price as different grades have different properties and applications.
For example, OPC grade 53 has higher strength and durability than OPC grade 33 or PPC (Portland Pozzolana Cement), which makes it more suitable for high-rise buildings or heavy-duty structures.
Hence, OPC grade 53 tends to be more expensive than other grades.
Trends
The trends and developments in the global and domestic markets can also impact the cement price in India.
For example,the COVID-19 pandemic disrupted both demand and supply chains for many industries including cement resulting in lower production volumes and higher input costs which led to an increase in cement prices across many regions.
Similarly, the rising environmental concerns and regulations may also affect the cost.