Cements of unique characteristics for desired performance in a given environment are being manufactured by changing the chemical composition of OPC or by adding additives or by using different raw materials.
There are several types of cements available in the market. Each type of cement has its distinct properties. The applications of cement depend upon their unique properties which can be used in different construction and in engineering projects.
The following properties which have a huge impact on usage of cement are initial and final setting times, compressive strength, fineness and soundness.
Before starting the topic let’s have a glance on the definition of some of the important properties of any type of cement. A small note on the properties are given below:
Initial setting time
It is defined as the time taken for the cement paste to begin setting after the addition of water. In this time, the cement changes from plastic consistency to solid state.
Usually the initial setting time ranges from 30 min to several hours depending upon the type of cement.
Final setting time
It is defined as the time taken by the cement paste to fully harden and develop its full strength after it has been mixed with water.
It varies depending on various factors such as the type of cement, amount of water used and the temperature and humidity of the environment. Usually final setting time ranges from several hours to several days depending upon the type of cement.
Compressive strength
It is a measure of its ability to withstand the compressive load without breaking or cracking. The compressive strength of cement varies depending on various factors such as the type of cement, the water-cement ratio, the curing conditions, and the age of the concrete.
In general, the compressive strength of cement increases as it ages, with most of the strength gain occurring in the first 28 days after the cement has been mixed with water.

Fineness
The degree of fineness of cement is the measure of the mean size of the grains in it. It is an important property as it affects workability, strength and setting time of cement. It also helps in determining the quality and consistency of the cement. Cement which is too coarse may result in uneven setting and decrease in strength whereas cement too fine results in increased shrinkage and cracking.
Soundness
It is defined as the ability to maintain its volume and resist cracking and deformation after it has hardened.
The soundness of cement is an important property as it affects the long -term durability and strength of the structure.
Cement that exhibits excessive expansion indicates the presence of unsoundness, which can be caused by various factors such as excessive amounts of magnesia or free lime, or the presence of compounds such as gypsum.
Unsound cement leads to cracking and other structural problems in the finished structure.
In this blog, let’s discuss the properties of different types of cement and their usage.
Rapid Hardening Portland Cement
Properties
| Initial setting time | 30 minutes (minimum) |
| Final setting time | 10 hours (maximum) |
| Compressive strength | |
| 1 day | 16 N/mm2 |
| 3 day | 27.5 N/mm2 |
Uses
It is used when load is applied in a short period of time. It is most suitable for repair of roads and bridges.
High Alumina Cement
Properties
| Initial setting time | 30 minutes (minimum) |
| Final setting time | 600 min (maximum) |
| Compressive strength | |
| 1 day | 30 N/mm2 |
| 3 day | 35 N/mm2 |
Uses
It is used as a refractory concrete in industries and also widely used for precasting. It is resistant to the action of fire, sea water, acidic water and sulphates.
Super sulphated portland cement
Properties
| Initial setting time | 30 minutes (maximum) |
| Final setting time | 600 minutes (maximum) |
Compressive strength

Uses
It is generally preferred in hydraulic engineering constructions such as RCC
pipes in ground water, concrete structures in sulphate bearing soils, sewers carrying industrial effluents.
Sulphate Resisting Portland Cement
Properties
| Initial setting time | 30 minutes (minimum) |
| Final setting time | 600 minutes (maximum) |
Compressive strength

Uses
It is used where concrete is exposed to deterioration due to sulphate attack such as concrete in contact with soils or ground waters containing excessive sulphate as well as concrete in sea water or exposed directly to sea- coast.
Portland Slag Cement

Properties
| Initial setting time | 30 minutes (minimum) |
| Final setting time | 10 hours (maximum) |
Compressive strength

Uses
This cement is used for mass concreting such as for dams, foundations etc
Low Heat Portland Cement
Properties
| Initial setting time | 60 minutes (minimum) |
| Final setting time | 600 minutes (maximum) |
Compressive strength

Uses
It is mostly suitable for large mass concrete works such as dams and also used for raft foundation.
Portland Puzzolana Cement
Properties
| Initial setting time | 30 minutes (minimum) |
| Final setting time | 600 minutes (maximum) |
Compressive strength

Uses
It has low heat evolution. It can be used in places of mass concrete such as dams and in places of high temperature.
Quick Setting Portland Cement
Properties
| Initial setting time | 5 minutes |
| Final setting time | 30 minutes |
| Compressive strength | |
| 1 day | 17-48 N/mm2 |
| 3 day | 24-69 N/mm2 |
Uses
It is used where repairing of concrete is required, precasting concrete products, and in underwater construction.
Masonry Cement
Properties
| Initial setting time | 90 minutes (minimum) |
| Final setting time | 24 hours (maximum) |
| Compressive strength | |
| 7 days | 2.5 N/mm2 |
| 28 days | 5 N/mm2 |
Uses
It is used where high strength mortar is required. It is particularly used in structures that need to withstand high levels of stress such as retaining walls, foundation walls, chimneys etc.
Water repellent Cement
Properties
Compressive strength

Uses
This type of cement is used in basement and foundation walls, roofs and exterior walls, swimming pools, marine structures, and tunnel linings.
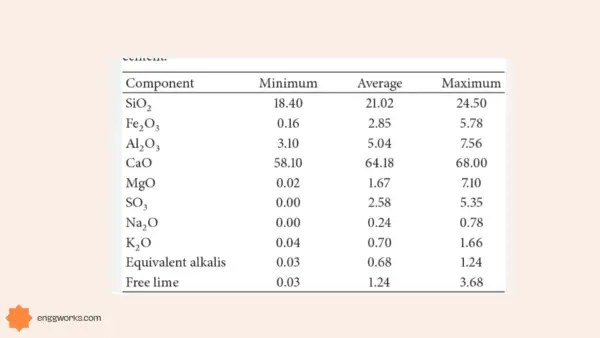
PHYSICAL properties of various types of cement

Source : Concrete Technology by M.S.Shetty
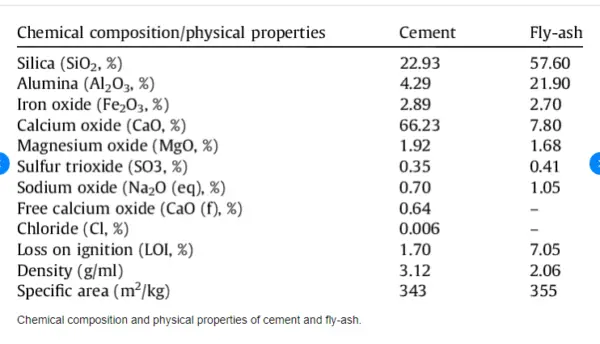
CHEMICAL properties of various types of cement

Source : Concrete Technology by M.S.Shetty