The physical properties of cement play a crucial role in determining the quality and suitability of cement for making concrete.
Cement is one of the most widely used construction materials in the world. It is one of the most important materials used in construction and civil engineering projects. It is a fine powder made from limestone, clay, and other ingredients that hardens when mixed with water
There are several tests that help determine the key physical properties of cement and whether it has the desired characteristics to produce good quality concrete.
important physical properties of cement
Physical properties of cement is important to ensure it will impart the necessary concrete physical properties like workability, strength, dimensional stability, and durability.
- Fineness of cement: This refers to the size of the particles of cement. The finer the cement, the more surface area it has for hydration and bonding. Fineness of cement can be measured by sieving, air permeability, or Blaine’s method. Finer cement also requires more water for mixing and may cause higher heat of hydration and shrinkage.
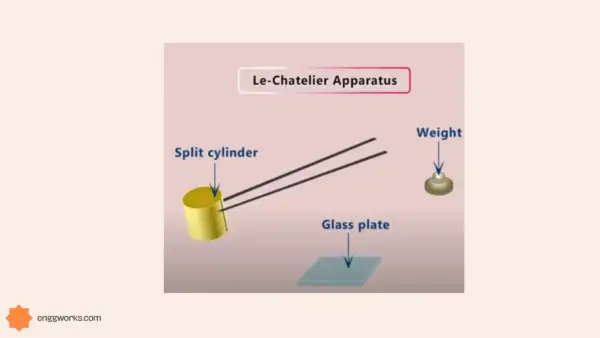
- Soundness of cement: This refers to the ability of cement to not shrink or crack upon hardening. Soundness of cement depends on the amount and type of impurities present in it, such as free lime, magnesia, or sulphates. Soundness of cement can be tested by Le Chatelier’s method or autoclave method. Sound cement should not show any significant expansion or distortion after setting.
- Consistency of cement: This refers to the fluidity or plasticity of cement paste. Consistency of cement affects its workability and strength. Consistency of cement can be measured by Vicat’s apparatus or flow table test. The standard consistency of cement is the amount of water required to produce a paste that can penetrate a Vicat plunger to a depth of 5 to 7 mm.
- Setting time of cement: This refers to the time required for cement paste to start and finish hardening. Setting time of cement depends on the composition, fineness, temperature, and water-cement ratio of the mix. Setting time of cement can be measured by Vicat’s needle or Gillmore’s needle. The initial setting time of cement is the time when the paste can resist a slight pressure, while the final setting time is the time when the paste can resist a moderate pressure.
- Strength of cement: This refers to the ability of cement to resist various forces such as compression, tension, shear, or bending. Strength of cement depends on many factors such as curing conditions, age, water-cement ratio, admixtures, and aggregates. Strength of cement can be tested by various methods such as compressive strength test, tensile strength test, flexural strength test, or modulus of rupture test. The most common test for strength of cement is the compressive strength test, which measures the load-bearing capacity of a standard cube or cylinder of hardened cement.
Cement Physical properties
Evaluating the physical properties of cement through standardized tests is essential to ensure production of good quality cement that will lead to strong, durable concrete for construction.
The physical properties of cement are listed below:
- Fineness
- Consistency
- Setting time
- Soundness
- Strength
- Heat of Hydration
- Specific gravity
- Bulk density
Fineness
- It is an important property as it affects the setting time, strength and workability of cement.
- It is a measure of its grain size and can be measured by using any of the three methods which are sieve analysis, air permeability method and sedimentation method.
- It is calculated as the specific area, which is the total surface area of the particles per unit weight of cement.
- Specific surface of the OPC and PPC should not be less than 2250 cm2/gm and 3000 cm2/gm.
Consistency
- The main purpose of this property is to determine the percentage of water required to prepare the cement paste which is further used for various tests like setting time and strength tests.
- Inorder to determine the consistency of the cement, Vicat apparatus is used.
- A square needle which is attached to the plunger is released slowly over the cement paste surface, when the reading is 5mm-7mm from the bottom of the mould is the correct water-cement ratio to attain standard consistency.
Setting time
- The time required for the cement to harden and gain strength is known as the setting time.
- There are various factors which affect the setting time of cement such as temperature,humidity, type of cement and the percentage of water used in the mix.
- The initial and final setting time is determined by the Vicat apparatus.
- Initial setting time is the time interval between the addition of water to the cement and the stage where the needle penetrates 5 mm measured from the bottom of the mould.
- Final setting time is the time interval between the addition of water to the cement and the time taken for the needle to make an impression on the test block.
- Square needle is used for initial setting time whereas needle with annular collar is attached to the moving rod in the Vicat apparatus for final setting time.
- Initial and final setting time for ordinary cement are about 30 min and 10 hours.
Soundness
- It is defined as the ability to resist any volume changes which are caused due to physical or chemical reactions while in storage or in use.
- This property is important as it determines the free lime and magnesia present in cement so that the cement does not undergo any large change in volume after setting.
- Soundness of cement can be performed by any two methods which are Le-chatelier method or autoclave method.
- Unsound cement can result in cracks and disintegration of concrete.
- For OPC,PPC it is limited to 10mm.
Strength
Strength of cement plays a vital role in construction and building project works.
The two prominent properties of strength of cement are compressive strength and tensile strength.
Compressive strength
- It is defined as the ability to resist the load without any deformation or failure.
- The compressive strength of cement depends on the composition,fineness, curing, water-cement ratio and also on the age of the specimen.
- Compressive strength is obtained by placing the specimen in a compressive testing machine and applying load on the specimen.
- A mix proportion of 1:3 (1 indicates cement 3 indicates sand) should have a compressive strength of 16 N/mm2 for 3 days and 22 N/mm2 for 7 days.
Tensile strength
- It is defined as the ability to resist being pulled apart by external forces
- The tensile strength of cement depends on several factors such as the type and quality of cement,curing conditions, water-cement ratio and age of the sample.
- Tensile strength of cement is measured by the Briquette test method or by split tensile strength test.
- Tensile strength is much lower than compressive strength.
- Ordinary Portland cement should have a tensile strength of not less than 2 N/mm2 for 3 days and 2.5 N/mm2 for 7 days for a mix ratio of 1:3.
Heat of hydration
- It is defined as the amount of heat released when cement is mixed with water.
- It is usually measured by a calorimeter or thermocouple method.
- The heat of hydration of cement depends on its composition, fineness, water-cement ratio and temperature.
- Generally, higher heat of hydration cement has higher C3S and C3A content, finer particles, higher water-cement ratio and higher temperature than lower heat of hydration cement.
Specific gravity
- It is defined as the ratio of the weight of a given volume of cement to the weight of an equal volume of water at a standard temperature and pressure.
- It is measured using a pycnometer or a Le-chatelier flask.
- Specific gravity of cement affects several factors such as water-cement ratio, heat of hydration,consistency and quality of cement.
- The typical range of specific gravity for ordinary Portland cement is 3.10 to 3.25.
Bulk density
- It is defined as the mass of the cement per unit volume in loose state.
- It depends on various factors such as grain size, surface area of the particles and the degree of aeration of the cement particles.
- The bulk density of ordinary cement ranges from 1100 to 1500 kg/m
3
Testing the physical properties of cement is crucial to ensure the production of good quality concrete with the desired concrete physical properties like workability, strength, dimensional stability, and durability. It has to meet certain specifications for it to be useful in concrete for construction.