Cement is a powdery substance obtained by grinding a mixture of limestone ,clay and other minerals and the mixture is then heated to a temperature of roughly 1,450 degrees Celsius.
It is a vital material in the field of civil engineering, serving as the binding agent in various construction applications. The chemical composition of cement plays a crucial role in determining its properties and performance. chemical composition typically consists of four main components: calcium oxide (CaO), silicon dioxide (SiO2), aluminum oxide (Al2O3), and iron oxide (Fe2O3).
The raw materials are converted through a procedure called calcination into cement clinker, a fine powder that is pulverized to obtain cement.
Cement’s main use is to combine various substances such as sand, gravel and water to create a solid, long-lasting substance.
It is an essential part of concrete, which is frequently used in building projects because of its strength, durability, and adaptability.
Ordinary Portland Cement
When combined with water, Portland cement, a type of hydraulic cement, hardens and sets.
It is created by grinding clinker, which is a mixture of gypsum, clay, and minerals like iron ore, limestone, and clay.
Portland cement is the most widely used type of cement in building because it is adaptable, readily available, and reasonably priced.

Chemical Composition
Ordinary Portland Cement consists primarily of two main ingredients which are argillaceous and calcareous materials.
Argillaceous materials mainly consist of silica, alumina and oxides of iron whereas calcareous materials consist of limestone.
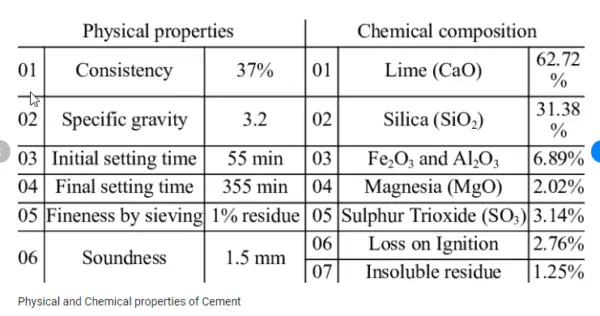
The chemical composition of cement with percentage can vary depending on the type of cement, but a typical composition of cement for Ordinary Portland Cement (OPC) includes approximately 60-67% CaO, 17-25% SiO2, 3-8% Al2O3, and 0.5-6% Fe2O3.The chemical compounds percentages are tabulated below:
| Ingredient | Chemical formula | Percentage |
| Lime | CaO | 60-67 |
| Silica | SiO2 | 17-25 |
| Alumina | Al2O3 | 3-8 |
| Iron Oxide | Fe2O3 | 3-5 |
| Gypsum | CaSO42H2O | 1-4 |
As per IS 269-1989 specifies the following chemical requirements for 33 grade cement which are given below:
The majority of Portland cement, which is frequently used as a binder in building materials like concrete, is made up of a group of four principal compounds known as the Bogues compounds.
These compounds are formed when the oxides present in the raw materials are subjected to high temperature mix with each other.

The four substances—tricalcium silicate, dicalcium silicate, tricalcium aluminate, and tetracalcium aluminoferrite—are named after their discoverer, R. H. Bogue.
These substances are crucial to Portland cement’s general functionality because they cause the cement to set and harden.
| Name of compound | Chemical Formula | Abbreviated Formula | Percentage by mass in cement |
| Tricalcium silicate | 3 CaO.SiO2 | C3S | 50 |
| Dicalcium silicate | 2 CaO.SiO2 | C2S | 25 |
| Tricalcium aluminate | 3 CaO.Al2O3 | C3A | 10-12 |
| Tetracalcium alumino ferrite | 4 CaO.Al2O3.Fe2O3 | C4AF | 8-10 |
Throughout the production process, these percentages can be changed to achieve various features and attributes in the completed cement product.
The bogue composition of cement is a method used to calculate the potential compound composition of cement based on its chemical analysis. This includes the bogue compounds of cement, which are formed during the cement manufacturing process and include tricalcium silicate (C3S), dicalcium silicate (C2S), tricalcium aluminate (C3A), and tetracalcium aluminoferrite (C4AF).
The bogue’s compound meaning refers to the specific compounds formed in the cement during the clinker burning process, which have a direct impact on the cement’s strength, setting time, and other properties.
Understanding the chemical composition of OPC and the bogue compounds of cement is crucial for civil engineers to select the appropriate cement type for their construction projects.