Stone masonry is one of the oldest construction techniques and has been used for centuries to build strong, durable structures. It involves stacking cut and dressed stones on top of each other, held together by mortar, to form walls, arches, and other architectural elements.
Masonry construction using natural stone continues to be popular today due to its aesthetic appeal, versatility, and resilience. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about stone masonry, its types, importance, applications, construction methods, tools, techniques, cost considerations, repairs, and more.
What is Stone Masonry?
Stone masonry refers to the building of structures from individual units of stones laid in and bound together by mortar.
The stones used could be either naturally occurring granite, limestone, marble, sandstone etc. or artificial stones like architectural terracotta. Based on the type of stone used, masonry is classified into granite masonry, limestone masonry, marble masonry etc.
Stones used for masonry construction are prepared by finely dressing them to regular shapes before being laid in the structure.
The dressed stone units are sometimes called as ashlars. Based on the dressing style, ashlars may be classified into rubble masonry, squared rubble masonry, coursed rubble masonry, and ashlar fine masonry.
The mortar binds the masonry units together, transfers load between them, and provides resistance against weathering effects and moisture. Cement mortar and lime mortar are commonly used. Admixtures like plasticizers might also be added to improve the properties of the mortar.
The basic principles used in stone masonry construction are similar to brick masonry. But the larger size of stone units provides enhanced strength, stability and durability compared to brick masonry.
Types of Stone Masonry
There are many different types of stone masonry, which are classified based on the stone dressing styles, pattern of arrangement of stones, and mode of construction. The common types of stone masonry are:
Rubble Masonry
This is the crudest type of stone masonry in which undressed stones of irregular shapes and sizes are used. The gaps between stones are filled with spalls and mortar to provide irregular surfaces. Rubble masonry is further subdivided into random rubble masonry, coursed rubble masonry, dry rubble masonry etc.
Ashlar Masonry
Ashlar masonry employs regular rectangular blocks of finely dressed stone neatly arranged in courses with very thin mortar joints. Based on stone dressing, ashlar masonry is classified into first class ashlar, second class ashlar and rusticated ashlar masonry.
Polygonal Masonry
Polygonal masonry uses dressed stones of irregular polygonal shapes laid in thick mortar joints. The joints are kept thick to compensate for irregularities in shapes.

Glass Block Masonry
This type of stone masonry uses glass blocks joined with mortar to construct translucent walls. The glass block masonry provides good thermal insulation, sound absorption and resistance to fire.
Ornamental Masonry
Various finely crafted ornamental stones are used here to provide decorative and architectural ornamentation in buildings.
Importance of Stone Masonry in Construction
Some of the important advantages of using stone masonry in construction are:
- Extremely strong, durable, and fire resistant
- Has high load bearing capacity
- Requires less maintenance compared to other materials
- Has superior sound absorption and insulation properties
- Aesthetically appealing due to availability of different stone textures and colors
- Ecologically friendly since it uses natural stones
- Can withstand weathering effects better than other materials
- Has longer service life spanning centuries
Due to these attributes, stone masonry has been used to construct large monuments, government buildings, residential premises, bridges, dams, and fortifications since ancient times. The thick massive walls provide stability, acoustic privacy, thermal insulation, and security.
Applications of Stone Masonry
The major applications of stone masonry in construction include:
- Constructing walls, columns, arches, floors, foundations of buildings
- Building dams, piers, retaining walls, reservoirs, tunnels, culverts
- Providing cladding or veneer surfaces for aesthetics
- Constructing compound walls, gardens, parapet walls
- Used in pavement construction
- Building earthquake resistant structures in seismic zones
- Restoration and repair work of historic monuments
Stone masonry is also used for ornamental purposes in walls, fountains, fireplace mantels, external stairs etc. due to the durability and visual appeal provided by natural stones.
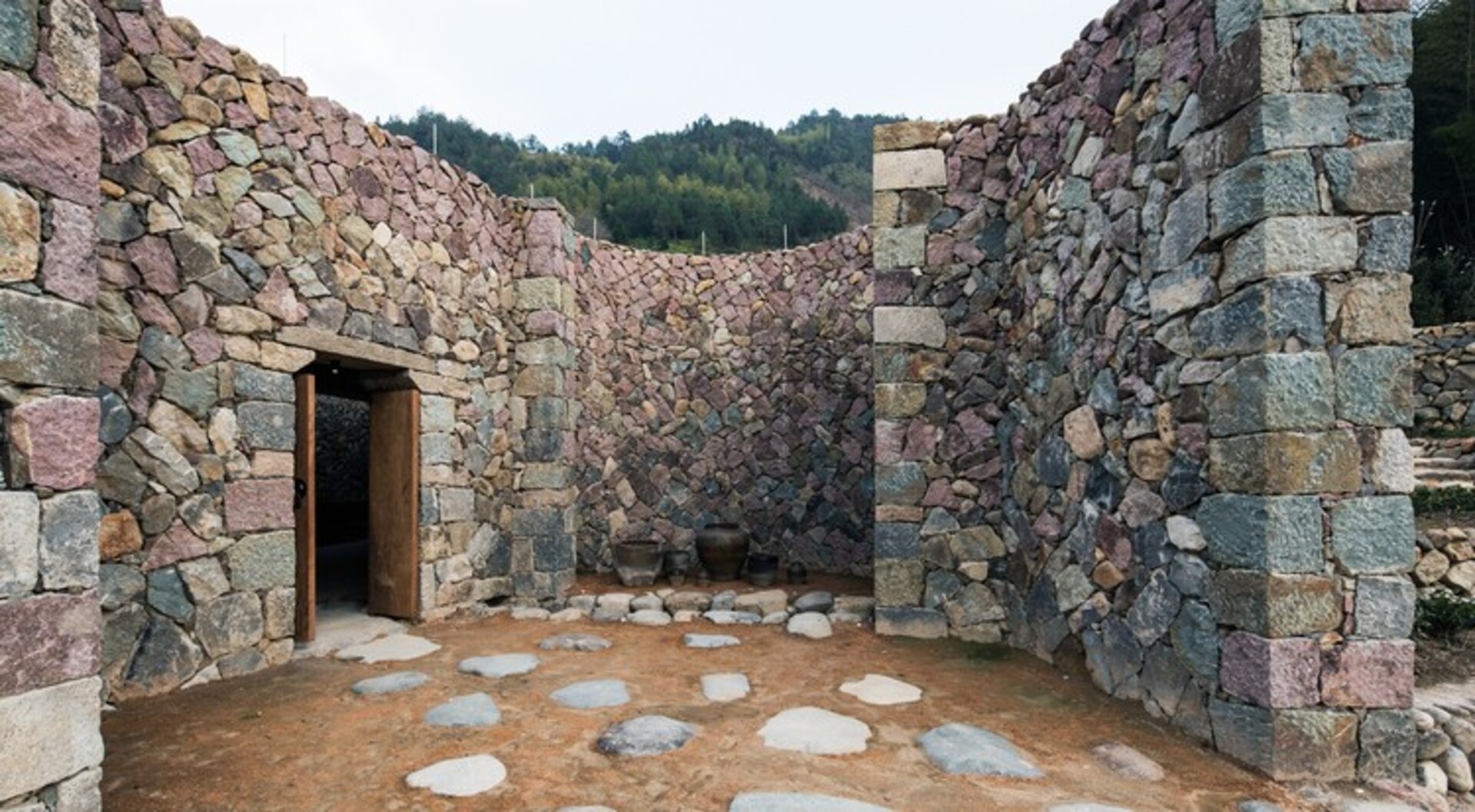

Stone Masonry Construction Methods
The commonly used methods for stone masonry construction are:
Regular Coursed Masonry
In this method, stones of equal height are arranged in courses or layers horizontally, with fine joints between stones. Vertical joints in each course are staggered with respect to the previous course. It provides a neat uniform appearance.
Uncoursed Random Rubble Masonry
This employs irregular undressed stones laid unevenly in mortar without forming courses. The work proceeds from bottom to top randomly. Low cost due to minimal stone dressing.
Dry Rubble Masonry
No mortar is used here. The irregular undressed stones are skillfully placed such that they remain in position due to their weight and frictional resistance. Common in hills and countryside.
Ashlar Fine Masonry
Employing fine dressed stones with very thin joints distinguishes this type. The ashlar stones are accurately cut to shape and laid in both horizontal and vertical joints. Gives a pleasing appearance.
Polygonal Masonry
Stones used are hammer dressed and have irregular polygonal shapes. They are laid in thick cement mortar joints to adjust the irregularities.
Glass Block Masonry
Clear glass blocks of standard size bonded together using cement, asphalt or other suitable adhesives. Reinforced glass blocks are also available. Provides aesthetic, insulating and sound proofing properties.
Composite Masonry
Combining dressed stones with other materials like bricks, tiles etc. arranged in decorative patterns constitutes composite masonry.
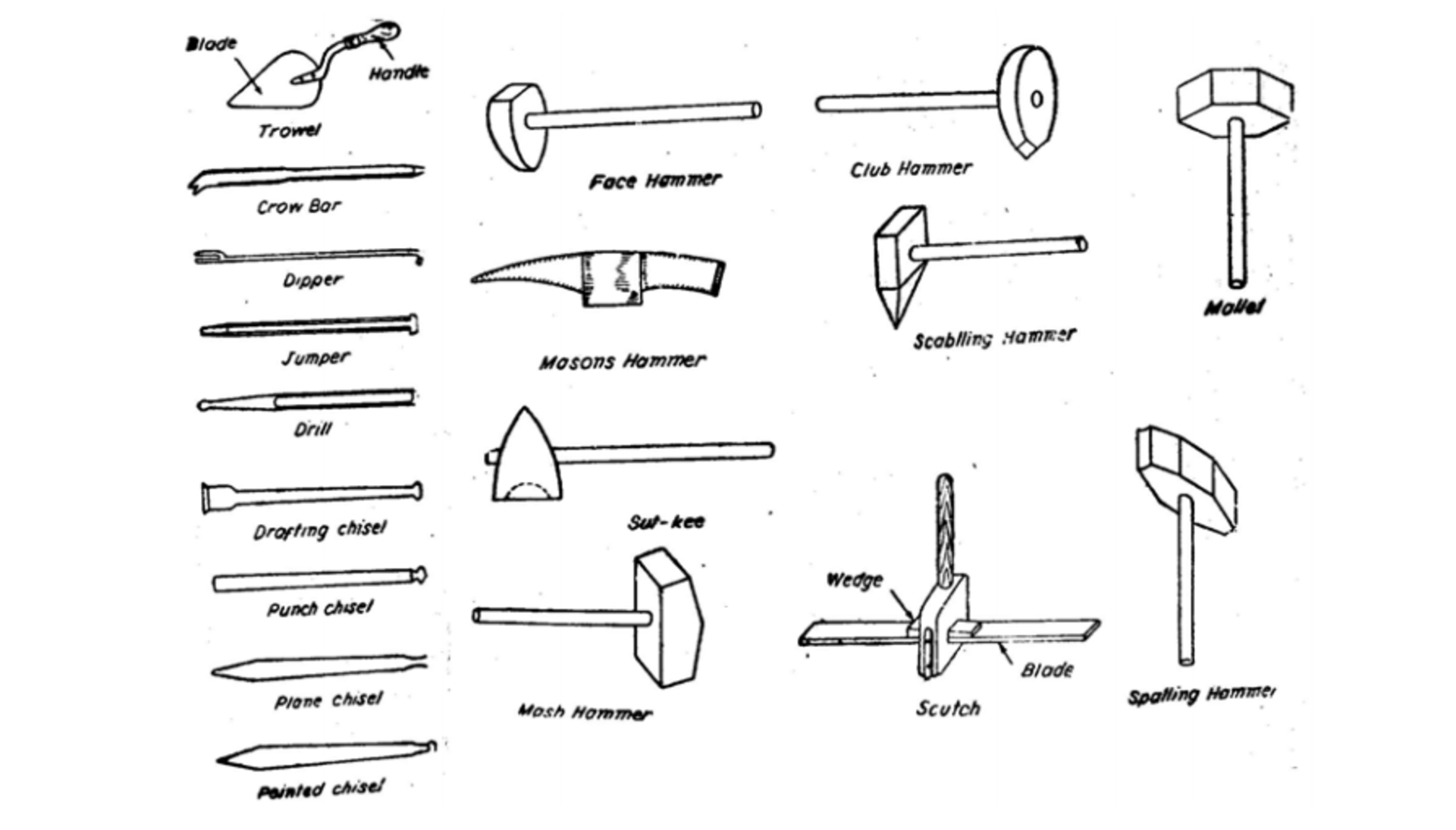
Stone Masonry Tools
The common tools used in stone masonry construction are:
- Mason’s Hammer – Used for dressing stones by chiseling. Many types like club hammer, stone hammer etc. exist.
- Mason’s Chisel – Inserted in hammer grooves and struck to chip off stone chunks for dressing. Different chisel types used.
- Lewis – Device to lift large dressed stones to position them in higher courses. Also called a lewis pin.
- Stone Spline – Thin piece of stone inserted in joint for alignment of successive courses. Also serves as a spacing shim.
- Plumb-bob, Leveling tools – Needed for vertical and horizontal alignment.
- Mason’s bevel square – Marks angles during stone dressing. Ensures proper geometric shaping.
- Straight edges – Used as guides when chiseling stones for achieving straight edges.
- Mortar pan, trowel and rake – Needed for mixing, placing and shaping mortar in joints.
- Grout pumps – Used to fill interior gaps in stones with grout. Achieves better structural strength.
Stone Masonry Techniques
Some important considerations in construction using stone masonry are:
- Quarrying of stones from suitable rocks like granite, sandstone etc. Dressing them to regular shapes.
- Proper selection and preparation of mortar. Cement or lime-based mortars commonly used.
- Laying dressed stones over mortar bed, tamping to ensure bonding, shaping joints.
- Ensuring proper vertical & horizontal alignment, resisting tendency to bulge out.
- Anchoring adjacent masonry to existing structures using ties and fasteners.
- Filling inner voids and gaps between stones using grouts for strength improvement.
- Curing masonry work by gentle water spraying without washing out mortar.
- Taking adequate precautions and safety measures during working at higher elevations.
Stone Masonry Cost
The cost of construction using stone masonry depends on the following major factors:
- Type and quality of stone used – expensive natural cut stones costs more
- Size of stones – Smaller stones sizes are cheaper as they require less cutting
- Dressing method – Fine dressing like ashlar masonry is costlier than rough rubble masonry
- Masonry pattern – Intricate bonding patterns cost more due to complexity
- Labor wages – Highly skilled masons charge more rates in developed countries
- Transportation costs – Natural stones quarried from remote locations incur higher charges
On average, the cost of stone masonry is around $900 – $1200 per cubic meter in USA and Rs. 1000 – Rs. 1500 per cubic feet in India. Caution must be exercised to avoid wastage of stone and mortar to reduce costs.
Stone Masonry Repair
Being exposed to weathering effects, moisture and temperature variations over long periods, stone masonry structures require periodic repairs and restoration to enhance their life span. Some common repair methods are:
- Replacement of damaged stones – Stones weakened due to weathering are replaced fully by new stones
- Pointing – Filling and sealing gaps in mortar joints with fresh mortar batch.
- Consolidation – Using ethyl silicates and other chemicals to restore integrity of decayed stones.
- Crack stitching – Filling cracks and voids in stones with grout or epoxy injections.
- Waterproofing – Coating masonry surface with waterproofing agents.
- Reinforcing – Inserting new steel rods, ties and clamps across cracks for strengthening masonry.
- Rising damp treatment – Creating moisture barriers, inserting chemicals into walls.
Stone Masonry Walls
Stone masonry is commonly used for constructing a wide range of walls in buildings and civil structures. Based on design needs, various types of stone walls are constructed:
- Retaining walls – Hold back earth and soils in retaining structures. Made thick with weep holes.
- Compound walls – Enclose premises to provide privacy and security against intruders.
- Boundary walls – Demarcate property lines between adjacent plots.
- Breast walls – Constructed along earth dams and embankments for stability.
- Parapet walls – Act as safety barriers along edges of buildings, balconies, bridges.
- Veneer stone walls – Have decorative facing of granite/marble stones over concrete backing.
Proper drainage arrangements are to be provided in all stone walls to avoid moisture damage. Weep holes help drain out water. Architectural elements like copings, pilasters, arches can be incorporated in stone walls based on aesthetics needs.
Stone Masonry Jobs
Stone masonry involves the following key jobs which require relevant skills and training:
- Stone selection & quarrying – Identify good quality construction stone visually. Safely detach blocks from quarries using wedges or wire saws.
- Cutting & shaping of stones – Cut irregular stones to regular sizes. Shape and dress the stones to required sizes using hammers & chisels.
- Laying & bonding of stones – Arrange stones in plumb over mortar beds. Tap stones gently for bonding. Fill mortar uniformly in joints. Remove excess mortar.
- Constructing architectural elements – Build stone arches, pillars, cornices, copings, staircases etc. based on structural design.
- Repairing old masonry – Identify distress like cracks, weathering. Carry out patching, sealing of gaps, strengthening.
- Supervising & inspecting – Inspect incoming stones regularly for defects. Supervise and guide junior masons during construction. Ensure quality standards.
Stone Masonry Contractors
Stone masonry construction requires skilled contractors undertaking the necessary jobs like:
- Sourcing good quality stones from quarries and preparing them for construction using stone dressing techniques.
- Preparing customized mortar mixes and grouts based on type of masonry.
- Laying stones accurately with proper bonding and alignment. Ensuring horizontal courses and plumb.
- Constructing structural and architectural elements with stone masonry including arches, pillars, walls, cladding etc.
- Restoring and repairing damaged stone masonry structures, monuments using specialized techniques.
- Providing cost estimates for the proposed masonry work and developing an optimal construction schedule.
- Ensuring availability of necessary tools, equipment and safety provisions at site for efficient masonry work.
Stone Masonry Materials
The main materials used in stone masonry construction are:
- Stones – Granite, limestone, sandstone, marble etc. Quarried from rocky outcroppings or alluvial deposits. Hardness varies from 800 to 1800 kg/cm2.
- Mortar – Binder material prepared using cement, lime, sand in suitable proportions. Admixtures can be added. Standard 1:3 and 1:6 mixes used.
- Grout – Thin low viscosity mortar used for gap filling. Could be neat cement or cement-sand grout. Provides additional strength.
- Reinforcement – Steel rods, ties and anchor bolts used for strengthening masonry.
- Coping & damp proofing materials – Stones, metals, bitumen used for surface protections.
- Safety gear – Helmets, boots, gloves, harness, goggles used by masons during construction.
Conclusion
Stone masonry is an ancient and time-tested construction form which continues to be popular and widely used today. The wide variety of stone types, shapes, textures and patterns provides great flexibility in masonry design.
When constructed properly using suitable stones, mortar and techniques, the resulting stone masonry structures are extremely strong, durable and resistant to weathering. Periodic repairs and maintenance helps to further enhance the lifespan of stone masonry assets.
This comprehensive guide has discussed all the important aspects related to principles, materials, methods and applications of stone masonry in construction.





