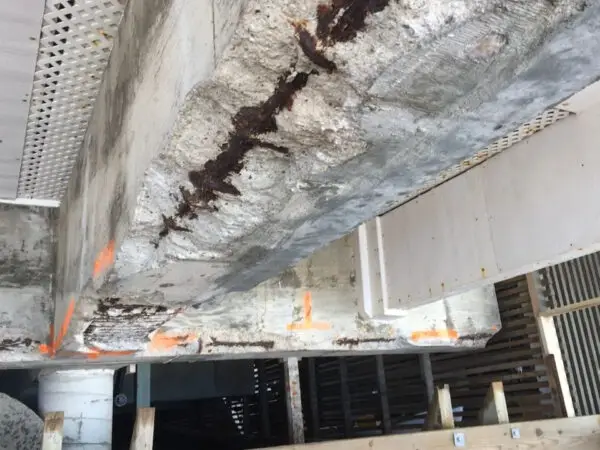
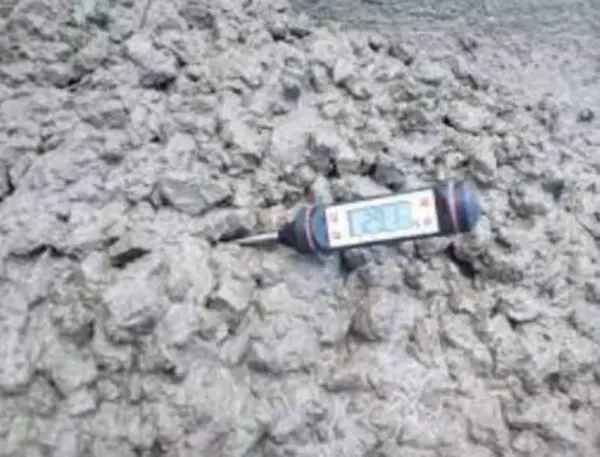
This is a very important property that determines the performance and durability of concrete in construction projects.
In particular, the 7-day of concrete strength is a key parameter that is often specified and tested to assess the early rate of concrete strength gain.
Concrete gains strength over time through the process of hydration, whereby cement particles react with water to form a rigid matrix that binds the aggregates together.
Typically, concrete strength is measured at 7 days after it has been cast and cured.
The 7-day concrete strength gives a good early indication of the potential 28-day strength of the concrete.
While concrete continues to gain strength after 7 days, around 65-70% of its 28-day strength is achieved at the 7-day mark.
Testing of concrete cylinders or cubes at 7 days helps to verify that the concrete has gained adequate strength to allow form work to be removed, for post-tensioning activities to proceed, or to put the concrete element into service.
If the 7-day concrete strength is much lower than the target, it may indicate potential problems with the concrete mix design or curing conditions.
Understanding early age strength development is useful for contractors to ensure construction activities are sequenced appropriately.
Specifications will often contain minimum 7-day compressive or flexural strength requirements that must be attained to meet compliance standards.
Overall, tracking 7-day strength provides quality assurance and allows assessment of the effectiveness of the selected concrete materials and mixtures.

Significance of 7-Day concrete Strength
The compressive strength of concrete at 7 days after placement provides a preliminary indication of the potential strength that can be achieved after 28 days, which is the reference strength used for structural design.
While strength continues to develop over time, the rate of strength gain begins to taper off after 7 days.
Research shows that on average, about 65-70% of the 28-day compressive strength is attained at 7 days under normal curing conditions.
Testing at 7-day concrete strength can verify if the mix design is gaining strength efficiently within the first critical week.
It also serves as a quality control check to detect problems early on, such as inadequate curing, incorrect batching of concrete at the plant, high water content, inaccurate test specimen preparation, molding and curing errors in the lab etc.
Specified 7-day concrete strength targets, usually around 70 percent of the 28-day strength, must be reached to ensure compliance with standards such as ACI 318.
Factors Influencing Early Age Strength
The strength developed by concrete in the first week is influenced by a combination of factors, mainly:
- Cement properties: Fineness, composition, mineral additives etc.
- Water-cement ratio
- Curing temperature: Higher temperatures accelerate strength gain
- Curing conditions: Adequate moisture prevents drying out
- Mix additives: Accelerators and water reducers improve early strength
- Admixtures compatibility
- Testing procedures: Sample preparation, curing and testing of specimens
Typical 7-Day Compressive Strength Values
For most structural concrete mixes, the typical compressive strength values at 7 days range between:
- 21 to 35 MPa for residential construction
- 35 to 48 MPa for commercial building construction
- 48 to 69 MPa for infrastructure such as bridges
High early strength concrete mixtures incorporating accelerators can reach higher strengths up to 48 MPa at 7 days.
Specialty pre-mixed and site-batched concrete can even attain strengths between 55 to 80 MPa at 7 days if properly cured.
However, for high-strength concrete mixes with specified 28-day target strength over 69 MPa, the relative 7-day strength is usually limited to about 55 to 65 percent of the 28-day value.
Testing Methods for 7-day concrete strength
The most common method for determining the 7-day compressive strength of concrete is by crushing strength test specimens, typically cylindrical samples measuring 150 mm diameter by 300mm height or 100mm cubes, prepared and cured in accordance with standards such as ASTM C31.
Specimens are tested in compression testing machines according to ASTM C39 specifications.
A minimum of three replicate samples are tested to check consistency. Flexural strength tests can also be conducted on beam samples.
Non-destructive testing methods such as the Windsor probe system provide a convenient alternative for estimating in-place strength.
However, they need accurate correlation to actual compressive strength test results for reliability.
Structural and Construction Implications
Specifying a target 7-day concrete strength has a dual significance from both structural design and construction viewpoints:
- Structurally, attaining certain early strength ensures adequate capacity to resist loads from removal of formwork, backfilling and early service loads.
- In terms of construction scheduling, confirming design strength at 7 days allows the structure to be put in service, allows staged construction to proceed, and productivity rates to be maintained as planned.
Preventing thermal cracking in large pours also requires tracking early-age strength gain using maturity meters to control cooling rate.
Specifications and Compliance
For structural concrete construction, ACI 301 specifies that the compressive test strength at 7 days should equal or exceed 70 percent of the specified 28-day target, unless otherwise approved by the engineer.
Minimum allowable 7-day concrete strength requirements are also sometimes detailed in project specifications by designers.
Failure to meet the prescribed 7-day concrete strength values signals potential deficiencies in concrete quality and triggers a need for evaluating changes to the mix design, increasing observation and testing procedures.
Quality Assurance
While strength testing at 7 days does help assess concrete supply and placement processes at a project, an adequately high 28-day strength remains the ultimate benchmark for structural adequacy.
As a quality assurance measure, maintaining historical plant production records of the ratio between 7-day and 28-day concrete compressive strength provides meaningful data to estimate later age strength, as this ratio remains fairly consistent for an established mix.
Variations greater than 10 percent in this ratio could indicate problems needing mix adjustments.
Conclusion
In summary, testing and documenting concrete compressive strength at 7 days provides a useful early quality check to ensure long-term concrete strength expectations can be fulfilled.
It also serves as an important construction aid for planning and allows timely corrective action if strength gain lags behind during initial curing stages, helping avoid structural issues at later ages.
Specifying an interim 7-day concrete strength target is now common practice for responsible concrete construction.